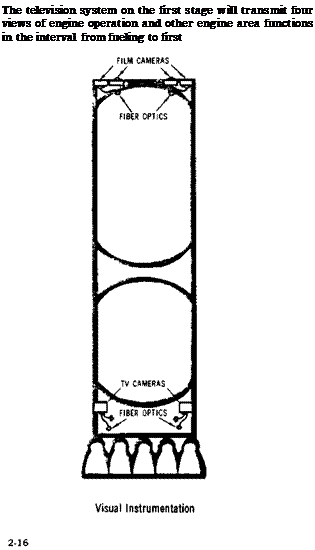
ENGINE CUTOFF
When the cutoff signal is initiated, the LOX dome operational oxidizer purge comes on. and the engine control valve stop solenoid is energized. Hydraulic pressure holding open the gas generator valves, the oxidizer valves, and the fuel valves is routed to return. Simultaneously, hydraulic pressure is directed to the closing ports of the gas generator valve, the oxidizer valves, and the fuel valves. The checkout valve is actuated and, as propellant pressures decay, the high level oxidizer purge begins to flow: then the igniter fuel valve and the ignition monitor valve close. Thrust chamber pressure will reach the zero level at about the same time the oxidizer valves reach full-closed.
|
|
|
WEIGHT: 95,000 lb. (dry)
1,037,0 lb. (loaded)
DIAMETER: 33 ft.
HEIGHT: 81 ft. 7 in.
BURN TIME: 6 min. approx, (actually 395 sec.)
VELOCITY: 15,300 miles per hour at burnout (approx.)
ALTITUDE AT BURNOUT: 114.5 miles
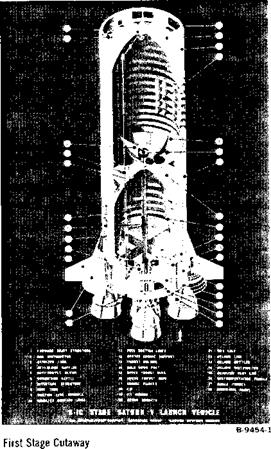
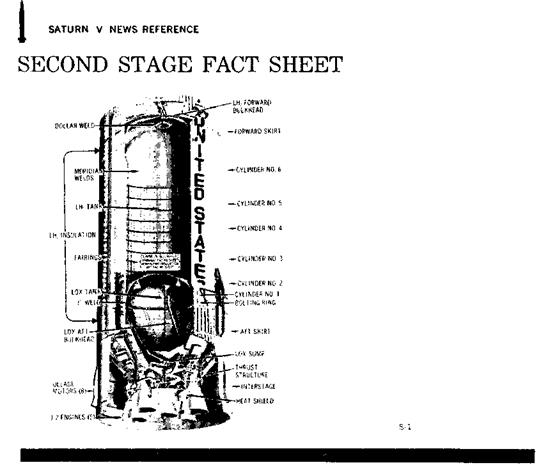
MAJOR STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS
AFT INTERSTAGE THRUST STRUCTURE COMMON BULKHEAD LH2 FORWARD BULKHEAD
AFT SKIRT AFT LOX BULKHEAD LH2 CYLINDER WALLS FORWARD SKIRT
MAJOR SYSTEMS PROPULSION: Five J-2 engines
Thrust: More than 1,000,000 lb. (225,000 maximum each engine)
Propellant: LH2~-260,000 gal. (153,000 lb.)
LOX 83,000 gal. (789,000 lb.)
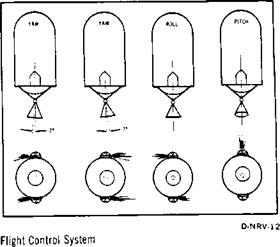
ELECTRICAL: 6 electrical bus systems, four 28-volt DC flight batteries, and motor-operated power transfer switches ORDNANCE: Provides, in operational sequence, ignition of eight ullage motors before ignition of five main engines, explosive separation of second stage interstage skirt, explosive separation of second stage from third stage, and ignition of four retrorockets to decelerate second stage for complete separation MEASUREMENT: Instrumentation, telemetry, and radio frequency subsystems THERMAL CONTROL: A ground-operated system that provides proper temperature control for equipment containers in the forward and aft skirt FLIGHT CONTROL: Gimbaling of the four outboard J-2 engines as required for thrust vector
control, accomplished by hydraulic-powered actuators which are electrically controlled from signals initiated in the flight control computer of the instrument unit (atop the Saturn V third stage)
і SATURN V NEWS REFERENCE












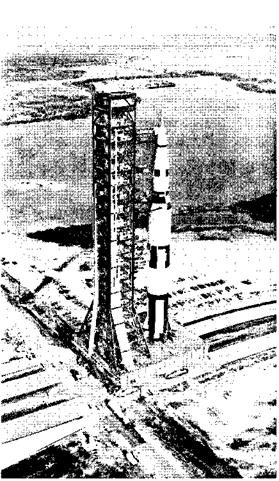
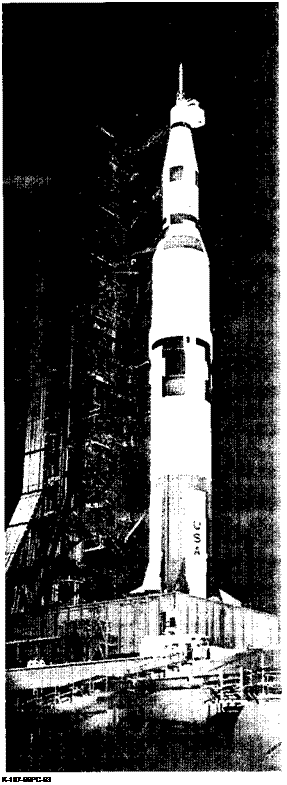
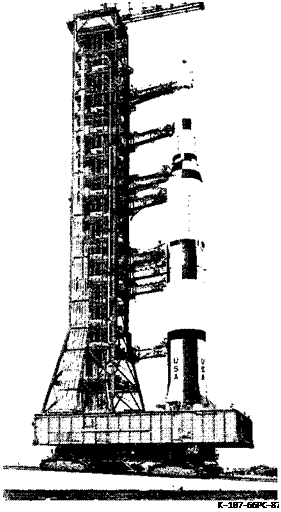 Facility Vehicle at Ramp of Launch Pad
Facility Vehicle at Ramp of Launch Pad