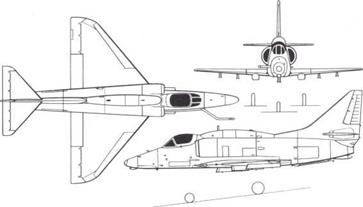
McDonnell Douglas A-4 Skyhawk
A-4A to A-4S and TA-4 series
Origin: Douglas Aircraft Co. El Segundo (now division of McDonnell Douglas, Long Beach). USA.
Type: Single-seat attack bomber: ТА, dual-control trainer.
Engine: (В, C. L, P. Q. S) one 7,7001b (3493kg) thrust Wright J65-16A single-shaft turbojet (US Sapphire): (E, J) 8.5001b (3856kg) Pratt & Whitney J52-6 two-shaft turbojet: (F, G, H, K) 9.3001b (4218kg) J52-8A: (M, N) 11,2001b (5080kg) J52-408A.
Dimensions: Span 27ft 6in (8 38m): length (A) 39ft 1 in; (B) 39ft 6in (42ft 10Jin over FR probe); (E, F. G. H. K, L, P, Q. S) 40ft 1 iin (12-22m); (M, N) 40ft 3Jin (1227m); (ТА series, excluding probe) 42ft 7^in (1 2-98m); height 1 5ft (4 57m); (early single-seaters 1 5ft 2in, ТА series 1 5ft 3in). Weights: Empty (A) 7.700lb; (E) 9,284lb; (typical modern single-seat, eg M) 10.4651b (4747kg); (TA-4F) 10,602 (4809kg); maximum loaded (A) 17,0001b; (B) 22,0001b; (all others, shipboard) 24,5001b (11,113kg); (land-based) 27.420lb (12,437kg).
Performance: Maximum speed (clean) (B) 676mph; (E) 685mph; (M) 670mph (1078km/h): (TA-4F) 675mph; maximum speed (4.000lb, 1814kg bomb load) (F) 593mph; (M) 645mph; initial climb (F) 5,620ft (1713m)/ min; (M) 8,440ft (2572m)/min; service ceiling (all, clean) about 49,000ft (14,935m); range (clean, or with 4,000lb weapons and max fuel, all late versions) about 920 miles (1480km); maximum range (M) 2,055 miles (3307km).
Armament: Standard on most versions, two 20mm Mk 12 cannon, each with 200 rounds; (FI, N, and optional on other export versions) two 30mm DEFA 553, each with 150 rounds. Pylons under fuselage and wings for total ordnance load of (А, В, C) 5,000lb (2268kg); (E, F, G, FI, K, L. P, Q, S) 8,200lb (3720kg); (M, N) 9,1551b (4153kg).
Flistory: First flight (XA4D-1) 22 June 1954; (A-4A) 14 August 1954, squadron delivery October 1956; (A-4C) August 1959; (A-4E) July 1961; (A-4F) August 1966; (A-4M) April 1970; (A-4N) June 1972; first of ТА series (TA-4E) June 1965.
Users: Argentina, Australia, Israel, Kuwait, New Zealand, Singapore, USA (Air Force in SE Asia, Navy, Marine Corps).
Development: Most expert opinion in the US Navy refused to believe the claim of Ed Fleinemann. chief engineer of what was then Douglas El Segundo, that he could build a jet attack bomber weighing half the 30,0001b
|
specified by the Navy. The first Skyhawk, nicknamed "Heinemann’s Hot Rod", not only flew but gained a world record by flying a 500km circuit at over 695mph. Today, more than 23 years later, greatly developed versions are still in production, setting an unrivalled record for sustained manufacture. These late versions do weigh close to 30.0001b, but only because the basic design has been improved with more powerful engines, increased fuel capacity and much heavier weapon load. The wing was made in a single unit, forming an integral fuel tank and so small it did not need to fold. Hundreds of Skyhawks have served aboard carriers, but in the US involvement in SE Asia "The Scooter" (as it was affectionately known) flew many kinds of mission from land bases. In early versions the emphasis was on improving range and load and the addition of all-weather avionics. The F model introduced the dorsal hump containing additional avionics, and the M. the so-called Skyhawk II, marked a major increase in mission effectiveness. Most of the TA-4 trainers closely resembled the corresponding single – seater, but the TA-4J and certain other models have simplified avionics and the TA-4S (Singapore) is a rebuild by Lockheed Aircraft Service with two separate humped cockpits and an integral-tank fuselage. Production of the M for the US Marine Corps continued in production to the 2,960th Skyhawk in February 1 979,
 Left: In no country has the Skyhawk seen more combat duty, nor suffered such heavy losses, as Israel. This A-4H (H for Hebrew) is typical of the large force which even today equip six combat – ready Heyl Ha’Avir squadrons.
Left: In no country has the Skyhawk seen more combat duty, nor suffered such heavy losses, as Israel. This A-4H (H for Hebrew) is typical of the large force which even today equip six combat – ready Heyl Ha’Avir squadrons.

Below: Launching a Shrike anti-radar missile from a ‘Camel’ (hump-backed A-4) from US Navy attack squadron VA-55 at the Pacific Missile Range.

















 1 I
1 I








 Right: One of the last of more than 600 Drakens was this TF – 35XD, one of six of this versatile two-seat dual-control version to be supplied to the Danish air force in 1968-73 along with 20 of the formidable 35XD single-seat version.
Right: One of the last of more than 600 Drakens was this TF – 35XD, one of six of this versatile two-seat dual-control version to be supplied to the Danish air force in 1968-73 along with 20 of the formidable 35XD single-seat version.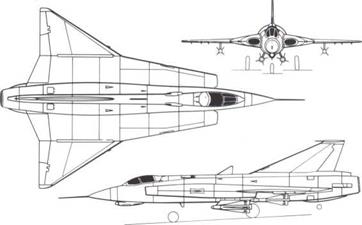
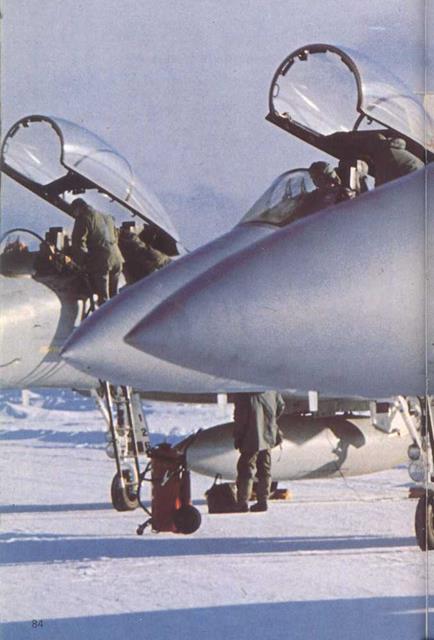
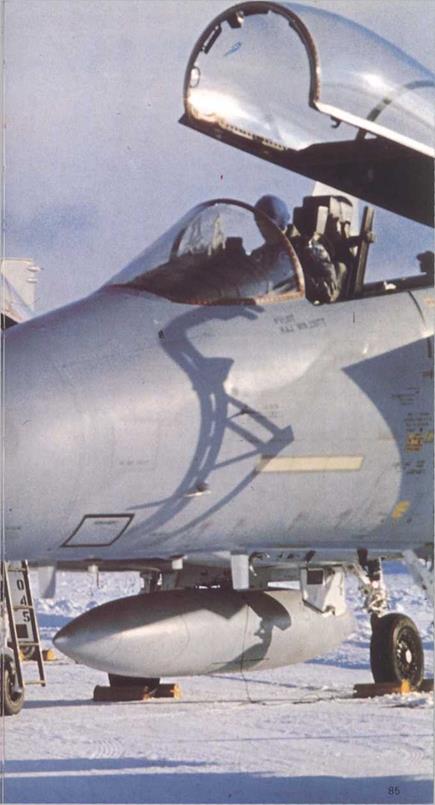




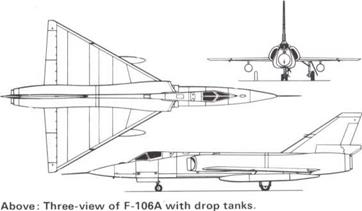








 Above: Start of a training sortie at a TAC base in the USA. Before takeoff the pilot will pivot the engine inlets downwards as seen in the photograph at left to match their shape to the angle of attack.
Above: Start of a training sortie at a TAC base in the USA. Before takeoff the pilot will pivot the engine inlets downwards as seen in the photograph at left to match their shape to the angle of attack.
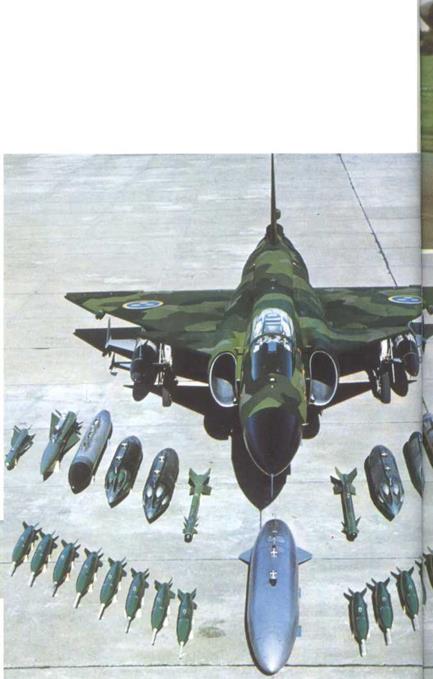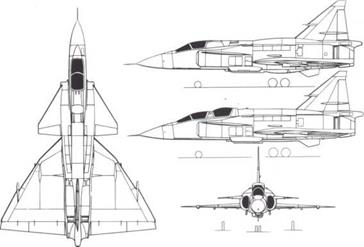

 proved as outstanding as it looked on paper in the 1960s, and even today no other Western European aircraft can rival it for radar performance, flight performance and short field length in all weathers. The latest Viggen variant, the JA37, is considerably different, with a new engine, very powerful gun. UAP 1023 pulse-doppler radar, digital automatic flight control system and extremely advanced inertial measurement and central computer systems. The development effort for the JA37 rivals that for the complete original aircraft, but with the help of a fleet of special-purpose test aircraft (some new and most rebuilds of early AJ and other models) the JA was cleared for production in 1976. By the start of 1 977 most of the initial batch of 30 were on the line, and service delivery is due in 1978. Eventually 200 are to equip eight squadrons.
proved as outstanding as it looked on paper in the 1960s, and even today no other Western European aircraft can rival it for radar performance, flight performance and short field length in all weathers. The latest Viggen variant, the JA37, is considerably different, with a new engine, very powerful gun. UAP 1023 pulse-doppler radar, digital automatic flight control system and extremely advanced inertial measurement and central computer systems. The development effort for the JA37 rivals that for the complete original aircraft, but with the help of a fleet of special-purpose test aircraft (some new and most rebuilds of early AJ and other models) the JA was cleared for production in 1976. By the start of 1 977 most of the initial batch of 30 were on the line, and service delivery is due in 1978. Eventually 200 are to equip eight squadrons.

