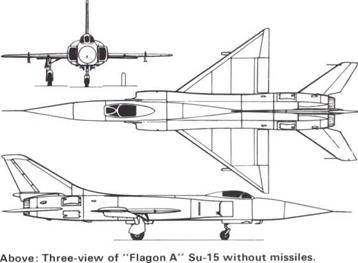
Sukhoi Su-15
Versions known to the West are code-named "Flagon-A to – E"
Origin: The design bureau of Pavel 0. Sukhoi, Soviet Union,
Type: Most versions, all-weather interceptor.
Engines: Two afterburning engines, believed to be Tumansky R-13F2 turbojets each rated at about 1 2.000lb (5443kg) dry and 1 5.875lb (7200kg) with afterburner.
Dimensions: Span (A) 31ft 3in (9-50m), (D) about 36ft (110m): length (all) 70ft 6in (21 -50m); height 1 6ft 6in (5 0m).
Weights: (Estimated) empty (A) 24,000lb (10,900kg), (D) 26,000lb (11,800kg): normal loaded (A) 35.275lb (16,000kg); maximum loaded (D) 46.0001b (21,000kg).
Performance: (Estimated) maximum speed at altitude, with two missiles, 1,520mph (2445km/h. Mach 2-3); initial climb 35,000ft (10,670m)/min, service ceiling 65,000ft (19.800m) combat radius 450 miles (725km); ferry range about 1,400 miles (2250km).
Armament: Two underwing pylons normally carry one radar "Anab" and one infra-red "Anab"; two fuselage pylons normally carry drop tanks, often with a 23mm GSh-23 two-barrel cannon between them; other missiles such as AA-6 or AA-7 are probably now being carried (but not yet seen by the West).
History: First flight (Su-15 prototype) probably 1964: (production Su-15) probably 1967.
User: Soviet Union (PVO).
 |
Development: Following naturally on from the Su-11. and strongly resembling earlier aircraft in wings and tail, the Su-15 has two engines which not only confer increased performance but also leave the nose free for a large Al radar. The initial "Flagon-A" version entered IA-PVO Strany service in 1969. "Flagon-B" is a STOL rough-field version with three lift jets in the fuselage and a revised "double delta" wing. "Flagon-C" is the Su-15U dual trainer, "-D" is basically a "-ES" without lift jets, and "-E" has completely updated electronics and the same extended wing but with further leading-edge improvements; the latest and probably final version is "Flagon-F" with an ogival radome suggesting use of a larger
aerial and possibly a completely new radar. It has been speculated that some late examples have an internal gun. In 1971 a US official estimated that 400 Su-15 were in service, with production at about 15 monthly. In early 1976 an estimate of PVO establishment gave the number of all Su-1 5 versions in combat service as 600. Though small numbers have served in Warsaw Pact countries and, in 1973, in Egypt, all Su-1 5s are at present believed to serve with the IA-PVO. There has been speculation in the West that later models could carry the Fox Fire radar and AA-6 "Acrid" missiles of the MiG-25.

 |
Above: This experimental STOL aircraft appeared publicly in 1967. It introduced a compound-taper wing very similar to that on all versions now in service (‘Flagon-E’ and ‘-F’) as well as three lift jets in a special bay in the centre fuselage (note open lift-bay doors above fuselage). Normal Su-15s need a paved runway.
Left: IA-PVO officers clustered round the cockpit of one of the current operational versions, either a ‘Flagon-E’ or a ‘Flagon-F’, the latter having a modified radome. Rather un-Russian in having immense power but very little wing (relative to gross weight), about 1,000 of all versions are in use.










