1-250 / N
In early 1944 the GKO (state committee for defense) “gave comrades Yakovlev, Lavochkin, Mikoyan, and Sukhoi the responsibility to build jet aircraft.” During the meeting held in Mikoyan’s office to discuss this project, all the department managers (who knew very well that the USSR did not have a jet engine in production) decided to power their new fighter with a package unit consisting of a piston engine—a 1,214- kw (1,650-ch) VK-107A—and a special booster nozzle designed at the central institute for aeroengine construction (TsIAM) by a team led by Professor К. V. Kholshchyevnikov. In this rather odd assembly, the power delivered by the piston engine was shared between two “consumers": a propeller 3.1 m (10 feet, 2 inches) in diameter, and a compressor intended to feed a combustion chamber. This assembly was known as a VRDK (Vozdushno-Reaktivmy-Dopolnitelniy Kompressor: jet – propelled auxiliary compressor) or booster. For takeoff and cruise situations, the main consumer was the propeller. During these flight modes the compressor (driven by a reduction gear) ran at idle, and no fuel was pumped into the seven burners of the combustion chamber When dash speed was needed fuel was injected into the burners and ignited by spark plugs. The compressor was then clutched at its maximum speed, and the revolution speed of the propeller was reduced. This power package offered a total of 2,061 kW (2,500 ch) at 7,000 m (22,960 feet) that is, 1,067 kW (1,450 ch) from the VK-107A at rated power and 994 kW (1,350 ch) from the VRDK equivalent.
It was also possible to regulate the VRDK power by means of the adjustable nozzle at the rear of the combustion chamber. This nozzle was fitted with two eyelids controlled by hydraulic jacks. The VRDK was cooled by a water-vapor system that protected the fuselage structure and the cockpit against overheating. The water tank had a capacity of 78 1 (20.6 US gallons). The VRDK and the VK-107Aboth ran on gasoline. The VRDK operated like the compressor’s second stage of a supercharged piston engine, increasing the aircraft’s ceiling.
The wing had a trapezoidal planform and a thin profile. The fuel system was made up of three self-sealing bladder tanks, one in the fuselage in front of the cockpit (412 1 [109 US gallons]) and two in the center section of the wing (100 1 [26 US gallons] each). The main gear
|
|
The first 1-250 prototype or N-l was rolled out on 26 February 1945 just eleven months after the project received the go-ahead.
|
|
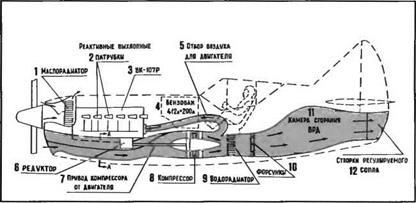
The 1-250 combined power unit (J) Oil cooler (2) Engine exhaust pipe (3) VK-107A piston engine (4) Fuel tanks of 412 and 200 1 (5) Engine supercharger air-bleed. (6) Reduction gearbox (7) Compressor drive shaft (8) Compressor (9) Water jacket. (JO) Fuel injectors (JJ) Combustion chamber. (J2) Adjustable-area nozzle.
was of the levered-suspension type with lower arms leading the leg. The most original features here were the doors, which permanently closed the wheel wells except at the very moment of the gear retraction or extension (a first in the USSR).
|
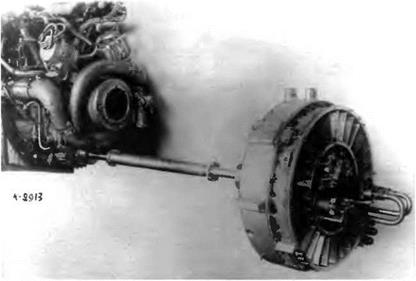
Left to right: the VK-107A engine, the compressor drive shaft, and the VRDK compressor |
The N-l prototype was armed with three 20-mm ShVAK (G-20) cannons—one mounted between the cylinder blocks and bring through the propeller hub, the others flanking the engine. Each of these weapons could Are 100 rounds, a flgure eventually improved to 160.
The preliminary design of the 1-250 was approved on 28 March 1944. At the same time, Sukhoi set to work on a similar aircraft, the Su-5 (1-107), which also had a combination power plant. But its performance was disappointing, and flight tests of the Su-5 were stopped on 15 July 1945. On 26 October 1944 the full-scale 1-250 mock – up was examined in great detail and endorsed; on 30 November almost all the sets of drawings were complete. As the war continued into 1945, OKB officials elected to build not an experimental prototype but instead an operational combat fighter.
Deputy chief engineer M. I. Guryevich had this to say in the OKB house newsletter:
We are now starting work on the N, an entirely new type of aircraft that greatly departs from our previous designs. We are going to reach speeds never achieved before. We are going to use new formulas, new materials. We shall have to create new systems. There is not a single sector, a single department of our OKB that will escape the difficult problems we shall have to face. We must give up all of the old configurations and all of the systems we are
|
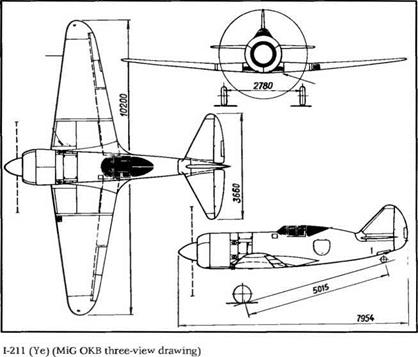
1-250 (N-l); the dotted line shows the modified fin (MiG ОКБ three-view drawing) |
used to and create new ones. We are forging ahead in a new way, the only one enabling us to achieve levels that have never before been attained and that we could hardly have dreamed possible.
The N-l was rolled out on 26 February 1945, less than one year after the project received the go-ahead, and the N-2 followed three months later. The initial prototype was first flown on 3 March 1945 by A. P. Deyev, and the VRDK was fired as early as the third flight. The
|
|
increase in speed proved to be significant: it was about 100 km/b (54 kt) faster than the best piston-engine fighter flying at the time. The only modification made involved a slight increase of the fin area.
In mid-May 1945 Deyev was killed during a flight test. The structural load factor was somehow exceeded, and the tailplane disintegrated at an altitude far too low for the pilot to bail out. The N-2 trials were conducted by a pilot from the LII, A. P. Yakimov, and later by two young ОКБ pilots, A. N. Chemoburov and I T Ivashchenko. During the first stages of the factory tests, the N-2 remained unarmed Flight tests showed that, at top speed, the plane’s yaw stability was inadequate. The fin area was increased accordingly. Takeoff roll was limited to 400 m (1,310 feet) with the VRDK in operation; but otherwise it took far too long to become airborne owing to the propeller’s small diameter. The N-2 was destroyed during a crash landing, with Chernoburov at the controls.
In June 1945 the production factory was instructed to build ten I- 250s in time for a Red Square flyover on 7 November in celebration of the twenty-ninth anniversary of the October Revolution. ОКБ test pilot I. T. Ivashchenko organized an accelerated training program for a batch of air force pilots under the command of Col. P. F. Chupikov. Nine I-250s were completed in time; unfortunately, the weather was so bad in Moscow on 7 November that the flyover had to be canceled.
Sixteen I-250s were delivered in record time to Baltic fleet aviation units at Skultye, near Riga. The first production I-250s had sabershaped propeller blades; they were replaced later on by conventional
|
The 1-250 N-l in 1945 with the larger fin. |
|
|
The N-2 the second 1-250 prototype, was rolled out in 1945 The fin was modified once more, and the tail wheel no longer retracts This aircraft was painted dark blue and embellished with a yellow streak.
|
|
This photograph of the N-2 shows the adjustable-area nozzle, two eyelids controlled by hydraulic jacks.
|
|
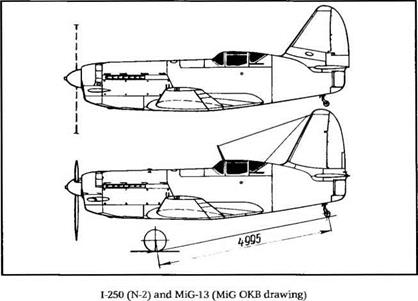
The production version of the 1-250 is sometimes referred to as the MiG-13. In fact, only sixteen aircraft of the type were delivered to the Baltic fleet aviation units.
|
|
The air intake duct for both the engine supercharger and the VRDK is visible below the engine mount of the MiG-13 Note also the saber-shaped blades of the propeller.
blades. The production 1-250 with serial number 3810102 (381 = factory number, 01 = first series, and 02 = second machine in the series) passed its factory tests in July 1947. Its acceptance trials were carried out at the Nil WS test center between 9 October 1947 and 8 April 1948 with I. M. Sukhomlin at the controls.
All production I-250s—referred to as MiG-13s in some ОКБ documents—were withdrawn from service in May 1948.
The following details refer to the 1-250 N-l.
Specifications
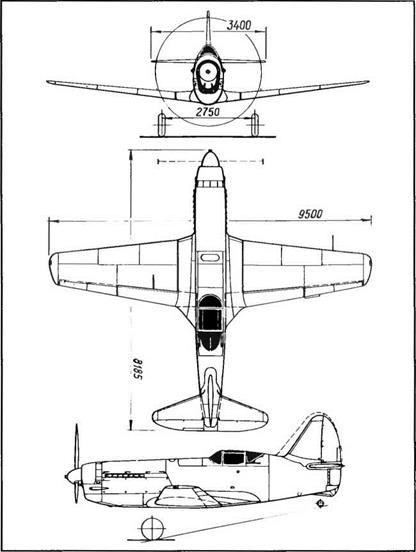
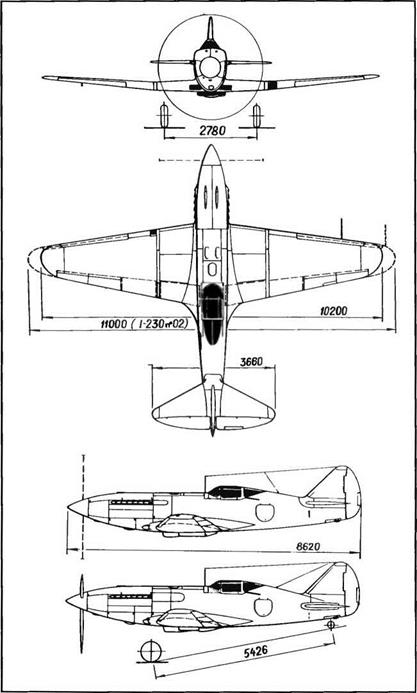
Span, 9.5 m (31 ft 1.9 in); length, 8.185 m (26 ft 10.2 in); wheel track, 2.75 m (9 ft 0.3 in); wheel base, 4.995 m (16 ft 4.6 in); wing area, 15 m2 (161 5 sq ft); empty weight, 2,587 kg (5,702 lb); takeoff weight, 3,680 kg (8,110 lb); fuel, 450 kg (992 lb); oil, 80 kg (176 lb); water, 78 kg (172 lb), wing loading, 245 kg/m2 (50.2 lb/sq ft); max operating limit load factor, 6.5.
Performance
Max speed, 825 km/h at 7,000 m (446 kt at 22,960 ft), max speed at sea level, 620 km/h (335 kt); climb to 5,000 m (16,400 ft) with VRDK in 3 9 min, without VRDK in 4.6 min; service ceiling with VRDK, 11,960 m (39,230 ft), without VRDK 10,500 m (34,440 ft); landing speed, 150 km/h (81 kt); range with VRDK, 920 km (570 mi), without VRDK 1,380 km (857 mi); takeoff roll with VRDK, 400 m (1,310 ft); landing roll, 515 m (1,690 ft).
The following details refer to the production 1-250 (MiG-13)
Specifications
Span, 9.5 m (31 ft 1.9 in); length, 8.185 m (26 ft 10.2 in); wheel track, 2.75 m (9 ft 0.3 in), wheel base, 4 995 m (16 ft 4.6 in); wing area, 15 m2 (161.5 sq ft); empty weight, 3,028 kg (6,674 lb); takeoff weight, 3,931 kg (8,664 lb); fuel, 590 kg (1,300 lb); oil, 80 kg (176 lb); water, 78 kg (172 lb); wing loading, 262.1 kg/m2 (53.7 lb/sq ft).
Performance
Max speed not recorded; unstick speed, 200 km/h (108 kt); landing speed, 190-195 km/h (103-105 kt).