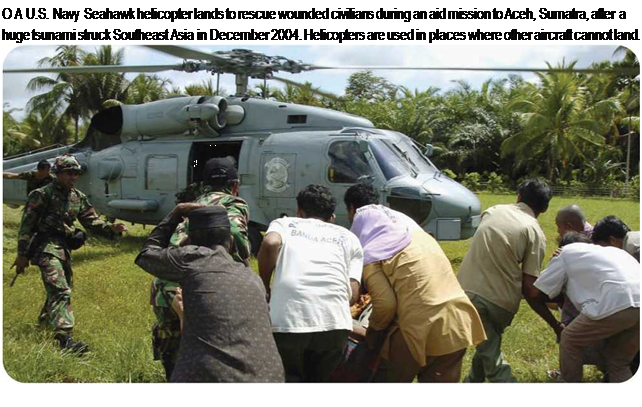
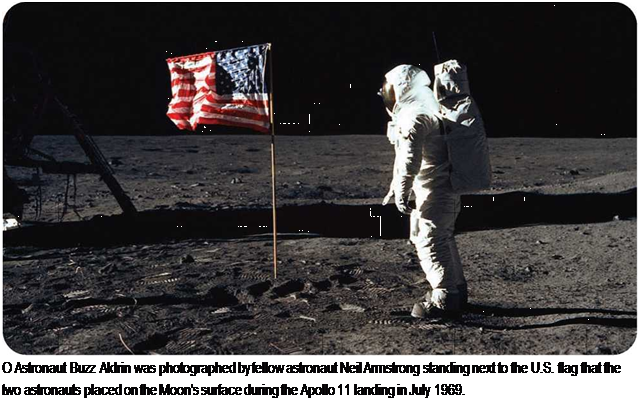
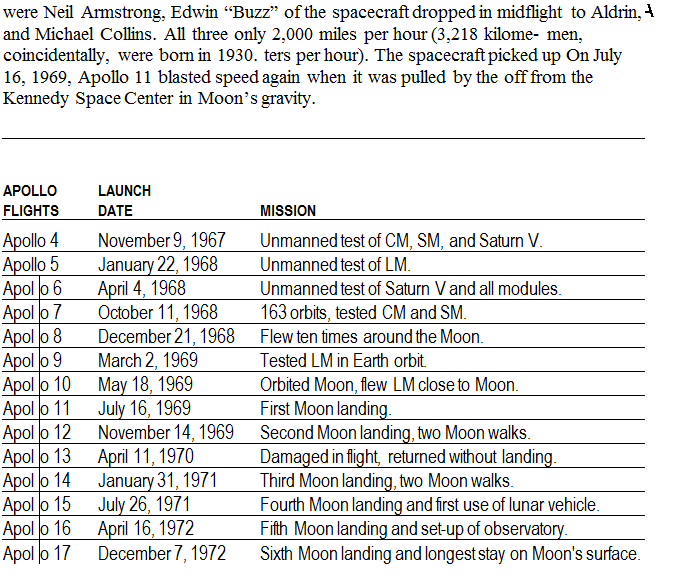
. Steering and Braking
There are several ways of steering a rocket or rocket-powered spacecraft. One way is to use swiveling fins, like an airplane’s control surfaces, in the atmosphere. A rocket must be traveling fast before its fins begin to work, because they only work when air is flowing over them very quickly. Other rockets have swiveling vanes in the rocket exhaust. When the vanes swivel, they deflect some of the engine’s exhaust jet. The entire jet can be deflected by swiveling the engine itself or just the nozzle. Most modern rockets have swiveling engines, also called gimbaled engines. The Space Shuttle’s main engines are gimbaled.
A rocket or spacecraft also can be turned or steered by means of thrusters.
When the Space Shuttle’s solid rocket boosters fall away, thrusters push them away from the spacecraft. The Space Shuttle uses forty-four thrusters in its nose and tail for attitude control when flying in space.
Rockets are used for braking as well as steering. Braking rockets also are called retro-rockets. When an orbiting spacecraft is ready to land, it fires off rockets in the direction in which it is traveling. The thrust slows the spacecraft, and gravity begins to pull it down.
 |
 |
The Soyuz spacecraft uses retro-rockets for landing. It fires retro-rockets just before it touches down on the ground to cushion its landing.














 includes details of alternate landing fields in case of emergency.
includes details of alternate landing fields in case of emergency.