Д Series
1-220 / A / MiG-11
In 1942 the ОКБ began to build a string of high-altitude interceptor prototypes (the A series) meant to oppose the Luftwaffe’s photo reconnaissance aircraft, which were able to operate with complete impunity because of their high operational ceiling. These Soviet aircraft were in fact updated remakes of the MiG-3.
|
The 1-220 no. 01 was first powered by the AM-38F engine at 1.250 kW (1,700 ch). |
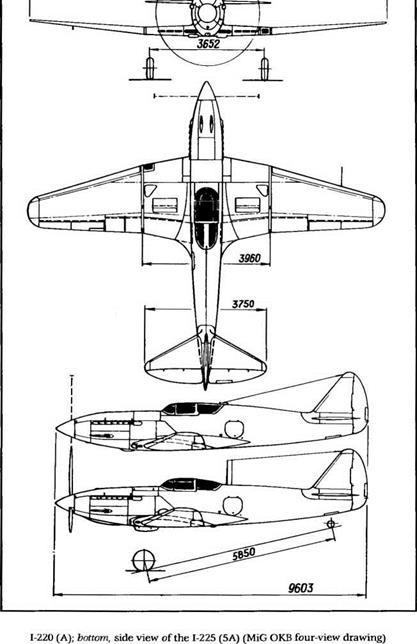
The first project was assigned the letter A and the designation 1-220. It was a low-wing single-seater of mixed construction. For the first time the ОКБ designers departed from the MiG-3 layout. All of their previous models had had the exact same span and wing area. The 1-220 was different: the radiator was moved to the wing center section (with air intakes in the leading edge and a variable shutter on the wing’s upper surface), the main gear legs were given a levered suspension system, its firepower was increased. Two prototypes were built. The 1-220 no. 01 received an AM-38F, which was later replaced by an AM-39. The AM-38F generated 1,251 kW (1,700 ch) at takeoff and 1,104 kW (1,500 ch) at rated altitude, while the AM-39 generated 1,325 kW (1,800 ch) at takeoff and 1,104 kW (1,500 ch) at rated altitude. Its armament included two synchronized 20-mm ShVAK (SP-20) cannons above the engine with 150 rpg.
Because flight tests and the development of the AM-39 took longer than expected, the 1-220 no. 02 received an engine that was not certified and could not yet be mass produced. Its armament was also different. It was the first Soviet fighter fitted with four synchronized 20-mm ShVAK (SP-20) cannons with 100 rpg and the first to have a whip antenna for its radio set.
The 1-220 no. 01 with AM-38F engine was rolled out in June 1943 and made its first flight in July with A. P. Yakimov in the cockpit. Tests continued through August and involved pilot P. A. Zhuravlyev. The 1-220 no. 01 with AM-39 engine was rolled out in January 1944 and

|
|
|
|
The 1-220 no. 02, powered by an AM-39, was rolled out in August 1944, but the high – altitude engine ratings were rather disappointing. |
underwent flight tests between then and August. The 1-220 no. 02 with AM-39 engine left the factory in August 1944 and was first flown by 1.1. Shelnest in September.
Development of a suitable engine for a high-altitude interceptor intended for PVO regiments proceeded concurrently with the preliminary design of the 1-220 and continued until the test flights ended in 1944. In the meantime, the notorious inadequacies of available engines at the edge of the stratosphere greatly complicated the work of the ОКБ. The wing loading of the 1-220 was relatively moderate and marked a significant improvement over the MiG-3 in terms of both maneuverability and rate of climb. But because no existing engine could provide the needed power, the design ceiling—the raison d’etre of this program—was never reached. At low and medium altitudes, however, the aircraft proved to be superior to the Yak and La “frontal" fighters then in use. For ground speed the 1-220 nos. 01 and 02 were between 30 and 70 km/h (16 and 38 kt) faster than the Yak-9. At 7,000 m (22,960 feet) the no. 02 was 50 to 95 km/h (27 to 51 kt) faster than the La-5. If the 1-220 had been mass-produced, it would have been called the MiG-11.
The following details refer to the 1-220 no 01 with the AM-38F engine/with the AM-39 engine.
|
|
Specifications
Span, 11 m (36 ft 1 in); length, 9.603 m (31 ft 6.1 in); height, 3.16 m (10 ft 4.4 in); wheel track, 3.652 m (11 ft 11.8 in); wheel base, 5.85 m (19 ft
2.3 in); wing area, 20.38 mz (219.37 sq ft); empty weight, 2,936/3,013 kg (6,471/6,641 lb); takeoff weight, 3,574/3,835 kg (7,877/8,452 lb); fuel, 335 kg (738 lb); oil, 45 kg (99 lb); wing loading, 175.4/188 2 kg/mz (35.9/38.5 Ib/sq ft).
Performance
Max speed, 630/668 km/h at 7,000 m (340/361 kt at 22,960 ft); max speed at sea level, 572/550 km/h (309/297 kt); climb to 6,000 m (19,680 ft) with AM-39 in 4.5 min; service ceiling with AM-38F, 9,500 m (31,160 ft); range, 960/630 km (595/390 mi).
The following details refer to the 1-220 no. 02 with the AM-39 engine.
Specifications
Span, 11 m (36 ft 1 in); length, 9.603 m (31 ft 6.1 in); height, 3.16 m (10 ft 4.4 in); wheel track, 3.652 m (11 ft 11.8 in); wheel base, 5.85 m (19 ft
2.3 in); wing area, 20.38 mz (219.37 sq ft); empty weight, 3,101 kg (6,835 lb); takeoff weight, 3,647 kg (8,038 lb); fuel, 335 kg (738 lb); oil, 45 kg (99 lb); wing loading, 178.8 kg/mz (36.7 lb/sq ft).
Performance
Max speed, 697 km/h at 7,000 m (376 kt at 22,960 ft); max speed at sea level, 571 km/h (308 kt); climb to 6,000 m (19,680 ft) in 4.5 min; service ceiling, 11,000 m (36,080 ft); range, 630 km (390 mi).