Space Shuttle
|
T |
he Space Shuttle was the world’s first reusable spacecraft and the first spacecraft with wings. The Space Shuttle can carry seven astronauts into space, stay in orbit for about two weeks, and then fly back to Earth to land on an airstrip.
The Shuttle Concept
Until the first Space Shuttle flew in 1981, all spacecraft (manned craft, satellites, and space probes) were launched by multistage rockets. Such rockets and the spacecraft they carried could be used just once. Only the spacecraft itself reached space; the discarded rocket stages fell into the sea or burned up in the atmosphere. The Space Shuttle was planned as a more economical vehicle
that could make regular trips into space. It has no rival. The Soviet Buran shuttle spacecraft, similar in appearance, made only one flight, without a crew, in 1988; it was thereafter canceled.
In 1969, a Space Task Group set up by President Richard Nixon’s administration suggested several new space projects. One was a reusable spacecraft, capable of flying one hundred or more missions. The result was the Space Shuttle, known to NASA as the Space Transportation System (STS). The main contractor was North American Aviation (later part of Rockwell International, now part of Boeing). Other contractors responsible for supplying the engines
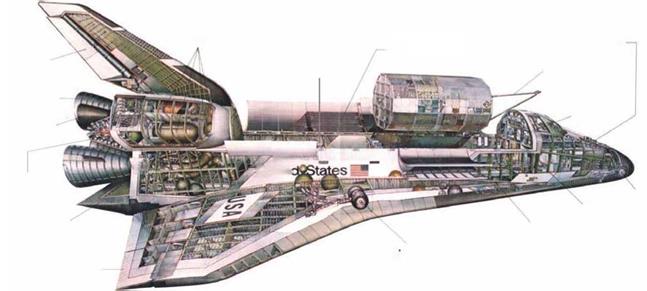
О A view inside the Space Shuttle shows the giant engines, the cargo bay, and the flight deck and mid-deck where the astronauts live.

|
|
||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
![]()
![]()
 Air
Air
control
thrusters
Electrical system fuel cells
|
|
|
|

and fuel tanks, were Morton Thiokol, Martin Marietta, and Rocketdyne.
The first Shuttle to fly was Enterprise, which was used for preliminary flight and landing tests from 1977. These tests included flights on top of a modified Boeing 747 airplane. Enterprise never actually went into space. Five Space Shuttles have flown in orbit. The first operational Space Shuttle, delivered to NASA in March 1979, was Columbia, which made its first space flight on April 12, 1981, and remained in service until it was destroyed in a tragic accident in 2003. Challenger, which arrived at Kennedy Space Center in July 1982, was the first Space Shuttle to be lost in an accident, in January 1986. The three Space Shuttles currently operational are Discovery, delivered in November 1983; Atlantis, delivered in April 1985; and Endeavour, which was built to replace Challenger and arrived at Kennedy Space Center in May 1991.










