Gudkov Gu-1
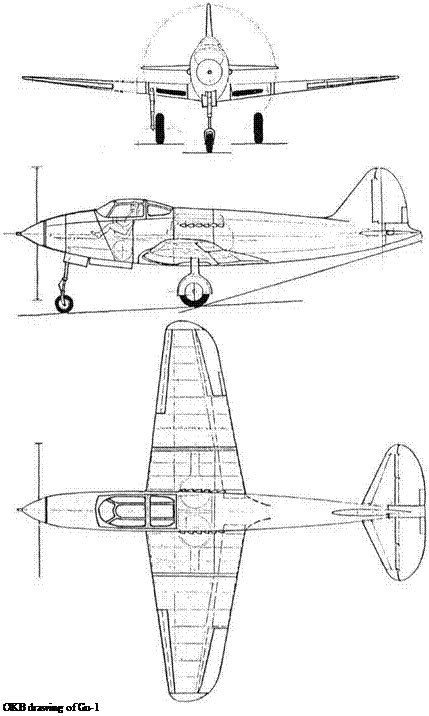
Purpose: To create a more manoeuvrable fighter.
Design Bureau: Brigade led by Mikhail Ivanovich Gudkov, Moscow.
Gudkov was one of the three partners who created the LaGG design bureau, later led by Lavochkin only. In early 1940 Gudkov became convinced that the Bell P-39 Airacobra, with the engine behind the cockpit, had a superior configuration. It gave the pilot a better view, and by placing the heavy engine in the centre of the aircraft greatly reduced the long
itudinal moment of inertia, and thus should improve manoeuvrability. As well as working on supposed improved derivatives of the LaGG, Gudkov managed to obtain funding for a mid-engined fighter in early 1942, as well as a contract with the A A Mikulin bureau for the supply of an engine. The resulting Gu-1, also called the Gu-37, was completed in the early summer of 1943. After prolonged taxi trials test pilot A I Nikashin said ‘It seems glued to the ground’. On 12th June 1943 Nikashin attempted the first flight. The Gu-1 reached about 200m (650ft) but then appeared to sideslip into the ground, Nikashin being killed. Gudkov’s brigade was disbanded.
The configuration followed the Airacobra exactly, with the major difference that the Gu-1 was constructed largely of wood, with bakelite-ply skin. Metal parts included the fuselage back to the firewall between the cockpit and engine (aligned with the front spar), which was based on a steel-tube truss with skin of removable Dl panels, Dl wing spars and Dl control surfaces. The wing was of 1V-10 Type V-2 aerofoil profile, and was fitted with automatic leading-edge slats and hydraulically driven split flaps. The engine was an AM-37 rated at l,380hp (the designer’s notes on the preliminary drawing show that he wanted an AM-41). Carburettor inlets were in the wing roots, and long inlets further outboard served the radiators inside the wing ahead of the inwards-retracting main landing gears. The drive was taken through a steel tube of 120mm (4%in) diameter to the reduction gear in the nose. The long nose gear retracted back into a bay in the lower part of the nose. Armament comprised a massive Taubin 37mm cannon firing through the propeller hub, fed by an 81 – round magazine (surprisingly large for this calibre) and six ShKAS machine guns in the fuselage and wing roots.
Few documents on the Gu-1 have been found. One is led to conclude that either the wing or vertical tail was too small, or possibly both.
|
Dimensions Span Length Wing area |
10.0m 10.68m 20.0 nf |
32 ft 9% in 35 ft 4% in 215ft2 |
|
Weights |
||
|
Empty |
3,742kg |
8,250 Ib |
|
Loaded |
4,610kg |
10,163 Ib |
|
Performance |
||
|
Landing speed (estimate) |
195 km/h |
121 mph |
|
No other data. |










