Grushin Sh-Tandem, MAI-3
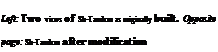
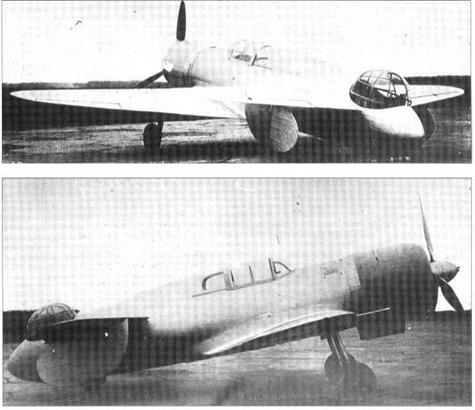
Purpose: To devise an improved configuration for a tactical attack aircraft. Design Bureau: Moscow Aviation Institute, designer Pyotr Grushin.
Born in 1906, Grushin worked on various aircraft at MAI, as well as a remarkable steam engine tested in a U-2 (Po-2). In 1935he began scheming a tandem-wing aircraft, thinking this could form the basis of an attack aircraft with a rear gun turret. The single example of the Sh-Tandem (Shturmovik-Tandem) was constructed in the Institute’s production training school. It was exhaustively tested by P M Stefanovskii from 5th December 1937. Once the dangerously inadequate directional (yaw) stability had been corrected, by adding fins and rudders above the tailplcine, the aircraft flew well. Eventually it was judged to be unreliable and not really needed, but a derivative with armour, an M-82 engine and a cannon in the turret might have proved very useful.
The key feature of this aircraft was that it had a main wing and a rear wing with 45 per cent as much area, both having R-l 1 aerofoil profile. After experimenting with elevens the control surfaces on the rear wing were linked to move in unison as elevators, all lateral control being by the ailerons on the main wing. Fins and rudders were fitted at 50 per cent of the semi-span on the rear wing, initially on the underside only in order to leave a clear 250° arc offire for the electrically driven turret with a ShKAS. Four more ShKAS were to be fixed firing ahead from the main wing, but these cannot be seen in photographs. An internal bay housed a 200kg (441 Ib) bombload. The engine was an M-87 (derived from the
|
Dimensions Span (main wing) (rear wing) Length Wing area (total) |
11.0m 7.0m 8.5m 30.4m2 |
36 fl 114 in 23ft 27 ft M in 327 ft2 |
|
Weights |
||
|
Empty |
not known |
|
|
Loaded given variously as |
2,560kg |
5,644 Ib |
|
and, more likely, as |
3,088 kg |
6,808 Ib |
|
Performance |
||
|
Max speed at sea level |
406 km/h |
252 mph |
|
at 4,200m (13,780 ft) |
488 km/h |
303 mph |
|
No other data. |
Gnome-Rhone K14) radial rated at 930hp. The tailwheel was fixed but the neat main units had single legs and retracted into the wing. The airframe was constructed mainly of wood, with skins of delta bakelite-impreg – nated veneer. Other features included a three-blade variable-pitch propeller, Hucks starter dogs on the propeller shaft, cooling
gills behind the engine cowling, a ventral ducted oil cooler (repeatedly modified) and aft-sliding pilot’s canopy.

 |
Despite its extraordinary appearance this aircraft was clearly basically successful. Whether a developed version could have done better than the Ilyushin Shturmovik is problematical.
GUDKOV Gu-1










