Spy in the Sky
FOR years a top secret, the existence of military spy planes made world headlines in 1960 when one was captured. Francis Gary Powers, American pilot of a U-2 reconnaissance jet, was caught spying1 over the Soviet Union and shot down.
The U-2 was designed in the 1950s, during the Cold War between the United States and Soviet Union. It was a long-winged, glider-like plane with a panoramic camera. Flying at high altitudes, it took photographs to search for Soviet ballistic missiles.
In the 1960s, another spy plane, the Lockheed SR-~1 Blackbird, was introduced. It could fly even higher and laster than the U-2 and photograph 100,000 square miles. The first stealth plane, it had a flattened shape and dark coating that helped it elude radar.
Today, both planes still fly missions to monitor world hot spots. By giving warning of dangerous conflicts, they help world leaders plan strategies.
Plying High
The Lotkheed U-2 is a hfgh – a titude reconnaissance jet. Its 80-foot wingspan^ives it lift to fly o. e’ 73,00C”eet.’t first flew over the Soviet _"’or n :re 19501s to pHotograph missi e activity.
U-2 Camera
 7vs U-2 Нусог В came’ayow г the Museum, took retailed ground pictures of Cuba, ike the one at top center in the ‘960s/ney revealed Soviet missiles, which iec to the Cuban Missile Cr sis.
7vs U-2 Нусог В came’ayow г the Museum, took retailed ground pictures of Cuba, ike the one at top center in the ‘960s/ney revealed Soviet missiles, which iec to the Cuban Missile Cr sis.

Lockheed SR-71
This high-altitude spy plane flies faster than any other aircraft. It set a speed record of 2,193 miles an hour. Like the U-2, it takes reconnaissance photographs. The plane’s shape and dark color earned it the name "Blackbird."
B-2 Stealth Bomber
One of the most technically advanced of all aircraft, the B-2 Stealth Bomber has a flying wing design and sophisticated computer technology. Its shape and dark coating help it penetrate enemy defenses without detection. First test flown in 1989, it served in the conflict in the Balkans.
 Global Hawk
Global Hawk
This experimental unmanned aircraft was developed by the Air Force. Its mission is to give military commanders a high-altitude, long-endurance system to photograph large geographic areas.
Fun Fact: Speedy Spy Plane
The SR-71 can fly at altitudes of 90,000 feet and as fast as Mach 3.3. It has set several speed records, including a flight between Los Angeles, California and Washington, D. C. in just 64 minutes!

JET power, first used in World War II, transformed the world of flight. With superior thrust, jet engines allowed planes to fly longer distances at higher speeds. In 1952, the First commercial jetliner, the British De I lavilland Comet, began service.
The Comet Hew 490 miles an hour, faster than any other passenger plane. Its 44 passengers traveled eight miles up in a comfortable pressurized cabin. Quiet jet engines made the ride smooth and relaxing. Yet in 1954, two Comets exploded in midair. The cause w as high-altitude stress on the plane’s metal body.

 |
 |
The next jet airliners were built with strong, pressure-resistant fuselages. I he American Boeing 707, introduced in 1957, was sale, fast, and comlortcible, with 145 seats. In 1969, Boeing built the lirst jumbo jet—the 747. I Ins became the world’s most successful jetliner. With a wide – body f uselage that can seat over 400, it lowered the cost of tur travel. Today, millions of people around the world have flown in the 747.
|
|
![]()
![]()
![]()



![]()

![]()

< Boeing 707
Sleek and streamlined, the Boeing /07 was the first II. S.jet transport airliner. It measured 144 feet long, with a wingspan of 130 feet. Flying nearly 600 miles an hour, it cut previous travel time nearly in half.
▼ The President’s Plane
Air force One, a Boeing 747, soars majestically ovei Mount Rushrnore, South Dakota. This plane carries the President of the United States on business around the world. It has a special interior for the President.
Concorde
The Concorde, developed by the British and French, is the world’s only supersonic jetliner. It first flew in 1969. Able to fly over twice the speed of sound, it could whisk passengers across the Atlantic in three and a half hours. The crash of an Air France Concorde in 2000 resulted in the grounding of all Concordes for safety testing

![]()
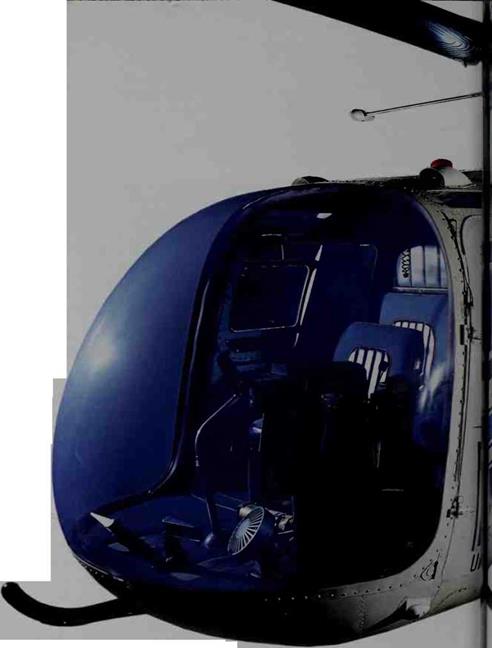 NLIKE fixed-wing airplanes, helicopters have
NLIKE fixed-wing airplanes, helicopters have
whirling rotary wings, called rotors. Helicopters can fly forwards, backwards, sideways, straight up or down, and hover in one spot. The idea of the helicopter is very old. The ancient Chinese had a toy helicopter, called a “flying top.” Early designers, including Sir George Cayley, inventor of the glider, envisioned helicopters. Yet it was not until much later that real helicopters appeared. In 1907, Frenchman Paul Cornu built anti flew a helicopter m the lirst free flight. The double-rotor craft rose five feet olf the ground for 20 seconds.
 |
 |
 |
The f li st practical single-rotor helicopters were invented by Igor Sikorsky in the 1950s. Since then, helicopters have performed many tasks other planes cannot. Because they can take off and land in small spaces and hover, helicopters serve as rescue craft, flying ambulances, lifting vehicles, and traffic observers. Modern helicopters range from small, light craft to heavy military gunships and transports.


![]()
![]()
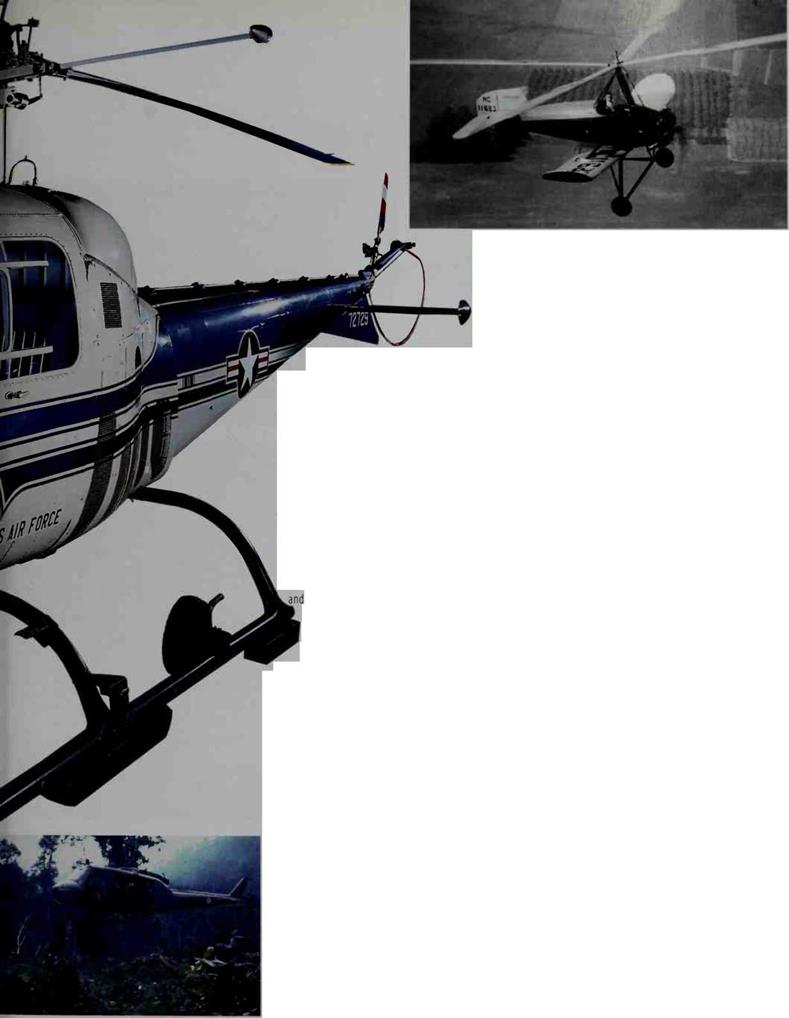
Autogiro
Invented in 1925, the autogiro (top) was a combination of an airplane and a helicopter. It used a propeller to move forward, but a wind-blown rotor for lift. The craft could not hover, but could use its rotor to fly very slowly.
Helicopter Commuter
New York Airways, the "first Helicopter Airline," offered early commuter service in this 15-passenger Vertol 44B helicopter. lt flew day and night between Manhattan La Guardia and Newark Airports. It carried passengers, freight, and mail. The helicopter also flew sightseeing flights.
► Firefighter
A large helicopter calleo an aircrane loads
2,0 gallons of water by a hose from a lake. It will fly to a raging forest fire in California. Crew aboard will use the water to help battle the fire.
Helicopter Rescue Team
A U. S. Coast Guard helicopter hoists rescue swimmer Jason Shepard back aboard after a day of training. Helicopters with trained crew fly in to save people trapped on sinking ships or stranded at sea.











