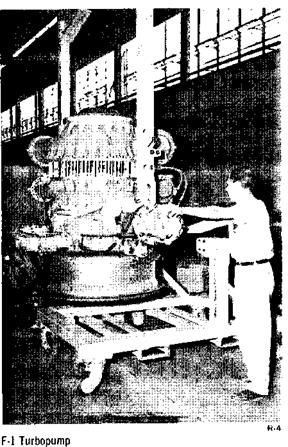
TURBOPUMP
The turbopump is a direct-drive unit consisting of an oxidizer pump, a fuel pump, and a turbine mounted on a common shaft. The turbopump delivers fuel and oxidizer to the gas generator and the thrust chamber. LOX enters the turbopump axially through a single inlet in line with the shaft and is discharged tangentially through dual outlets. Fuel enters the turbopump radially through dual inlets and is discharged tangentially through dual outlets. The dual inlet and outlet design provides a balance of radial loads in the pump.
|
|
Three bearing sets support the shaft. Matched tandem ball bearings, designated No. 1 and No. 2, provide shaft support between the oxidizer and fuel pumps. A roller bearing, No. 3. provides shaft support between the turbine wheel and the fuel pump. The bearings are cooled with fuel during pump operation. A heater block provides the outer support for No. 1 and No. 2 bearings, and is used during LOX chilldown of the oxidizer pump to prevent freezing of the bearings.
A gear ring installed on the shaft is used in conjunction with the torque gear housing for rotating
the pump shaft by hand, and also is used in conjunction with a magnetic transducer for monitoring shaft speed.
There are nine carbon seals in the turbopump: primary oxidizer seal, oxidizer intermediate seal, lube seal No. 1 bearing, lube seal No. 2 bearing, primary fuel seal, fuel inlet seal, fuel inlet oil seal, hot-gas secondary, and hot-gas primary seal.
The main shaft and the parts attaching directly to it are dynamically balanced prior to final assembly on the turbopump.