F-l ENGINE
ENGINE DESCRIPTION
The F-1 engine is a single-start. 1,500.000-pound fixed-thrust, bipropeliant rocket system. The engine uses liquid oxygen as the oxidizer and RP-1 (keroseneI as fuel. The engine is bell-shaped, with an area expansion ratio—the ratio of the area of the throat to the base—of Hi:L RP-1 and LOX are combined and burned in the engine’s thrust chamber assembly. The burning gases are expelled through an expansion nozzle to produce thrust. The five-engine cluster used on the first stage of the Saturn V produces 7.500,000 pounds of thrust. All of the engines are identical with one exception. The four outboard engines gimbal; the center engine does not.
The major engine systems are the thrust chamber assembly, the propellant feed system, the turbo-
|
|
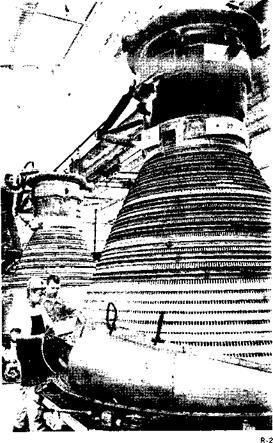
Assembly Thrust chambers of the F-i rocket engine—the most powerful engine under development by the United States – are assembled in this manufacturing line.
pump, the gas generator system, the propellant tank pressurization system, the electrical system, the hydraulic control system, and the flight instrumentation system.
THRUST CHAMBER ASSEMBLY
The thrust chamber assembly consists of a gimbal bearing, an oxidizer dome, an injector, a thrust chamber body, a thrust chamber nozzle extension, and thermal insulation. The thrust chamber assembly receives propellants under pressure supplied by the turbopump, mixes and burns them, and imparts a high velocity to the expelled combustion gases to produce thrust. The thrust chamber assembly also serves as a mount or support for all engine hardware.
Gimbal Bearing
The gimbal bearing secures the thrust chamber assembly to the vehicle thrust frame and is mounted on the oxidizer dome. The gimbal is a spherical, universal joint consisting of a socket-type bearing with a bonded Teflon-fiberglass insert which provides a low-friction bearing surface. It permits a maximum pivotal movement of <i degrees in each direction of both the X and Zaxes (roughly analogous to pitch and yaw! to facilitate thrust vector control. The gimbal transmits engine thrust to the vehicle and provides capability for positioning and thrust alignment.