POST MANUFACTURING CHECKOUT
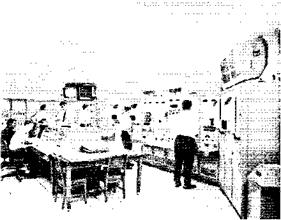
Before a booster leaves Michoud for test firing, its electrical and mechanical systems are tested extensively by Boeing technicians and engineers. The Stage Test Building with four giant test cells provides the facility. Inside the building are four control rooms, four computer rooms, and two telemetry rooms. These rooms house equipment that demonstrates the acceptability of the integrated systems of the booster. This includes telemeter calibration, continuity checks, and discrete-function monitoring. RF (radio frequency) also is evaluated.
|
8-7733-10 |
Moving—A’completed first stage is readied for post-manufacturing checkout.
Mechanical, hydraulic, and pneumatic systems tests are conducted to leak-check and functionally check the propellant systems and the engine complex. Checks then are performed to demonstrate the proper operation of the electrical and instrumentation systems. All systems are operated and checked individually and then checked as an integrated system in the automatic all-systems checkout.
|
B-9964-2 |
Monitoring—Technicians check booster performance during a simulated flight from a stage test control room.
After the operation of the test and checkout equipment is verified, all electrical, pneumatic, and hydraulic connections are made to the stage, resistance checks are run, and the stage undergoes physical examination.
The environmental control system is connected and checked for proper operation, and the stage’s electrical circuits are physically checked for resistance. Stage electrical power із applied in sequential steps and the distribution monitored. The stage instrumentation transmission system is checked out on both coaxial hardwire and RF links. The electrical systems checkout includes checks of the power distribution circuits, heater power subsystems, destruct system, sequencing subsystem, separation subsystem, and emergency detection system.
The range safety systems undergo a complete end – to-end checkout including transmittal of RF commands to the range safety command receiver and monitoring the arm, cutoff, and destruct signals generated by the system.
Instrumentation system testing during stage checkout includes: identification of data channels, gain adjustment of signal conditioners, and checks of measurement systems, telemetry systems, and operational RF systems.
|
SATURN V NEWS REFERENCE
|
|
First Stage in Test Cell
Pressure and leak checks are conducted on fuel and LOX tanks and associated lines, engines, fuel and LOX delivery systems, fuel and LOX pressurization systems, and the control pressure system. Checks are made of the calibration pressure switch simulation, fill and drain operation, and prevalve operation on both fuel and LOX systems.
Propulsion system checks include checks of firing command preparation and execution, engine shutdown prior to “launch commit,” malfunction cutoff, and normal propulsion sequences.
Most of the above-mentioned tests are run for a second time prior to static testing and again during post-static checkout.