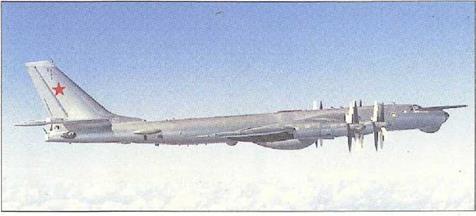
Tupolev Tu-95, Tu-142 ‘Bear’
|
|
T |
he first Tu-95/1 prototype of Tupolev’s extraordinary ‘Bear’ made its maiden flight on 12 November 1952. The swept-wing bomber had unheard of performance for a turboprop-powered aircraft. All of the early variants have now been retired, including the original Tu-95 and Tu-95M ‘Bear-А’ Tee-fall nuclear bombers (some of them converted as Tu-95U trainers). Various missilecarrying variants have also been retired, including the Tu-95K-20r and the refuelling-probe equipped Tu-95KD ‘Bear-B’, and the TU-95KM ‘Bear-C’ with an ECM tailcone. These variants had a broad undernose radome housing ‘Crown Drum’ guidance radar and carried AS-3 ‘Kangaroo1 missiles. The Tu-95K – 22 ‘Bear-G’ was externally similar but had a new "Down Beat’ radar and K-22 (NATO AS-4 ‘Kitchen’) missiles. The AV-MF’s Tu-95RT ‘Bear-D’ midcourse missile guidance/maritime radar recce platform has also been withdrawn, along with the long – range reconnaissance Tu-95R ‘Bear-EsT
The dedicated maritime reconnaissance/ASW Tu-142 ‘Bear-F’ incorporated several significant improvements, including a strengthened wing, a redesigned undercarriage, a fuselage plug, uprated NK-12MV engines and redesigned weapons bays. Four sub-variants had detail differences, but most
had a new cockpit with a raised roofline, and featured a new ventral radome housing a maritime search radar, About 55 ‘Bear-Fs’ remain in AV-MF (Russian naval aviation) service.
The sole export customer was the Indian Navy, which received eight Tu-142Ms. The Tu-142M ‘Bear-F’ also formed the basis of the Tu-142MR ‘Bear-Jr communications relay variant, which had an underfuseiage tracing wire antenna pod but no search radar, A total of 24 of these aircraft are in service.
The ‘Bear’ production line re-opened in 1983 to build 33 Tu-95MS-6 ‘Bear-H’ strategic bombers. This version was developed specifically to carry the new FSK-55 (AS-15 ‘Kent’) cruise missile. This was based on a shortened version of the Tu-142 airframe, but with a deeper, shorter radome and a new weapons bay accommodating a rotary launcher for six RK-55 missiles. Some 56 later aircraft (known as Tu-95 MS-16s) carry an add tional 10 RK-55s on underwing pylons, but these pylons were removed to comply with the provisions of the SALT and START treaties. The Tu-95MS remains in service with Kazakhstan (six aircraft) and Russia (68 deployed, 64 declared as missile carriers), but Ukraine’s aircraft are being scrapped.
 Specification: Tupolev TU-142M ‘Bear-F Mod 3’
Specification: Tupolev TU-142M ‘Bear-F Mod 3’
Powerplant: four 11033-kW |H,795-hp) KKBM (Kuznetsov) NK-12MV turbopreps _ Dimensions: wing span 51.10 m (167 ft Т/ in); length 47.50 m (155 ft 10 in) excluding IFfi probe and 49.50 m (’02 ft 4.8 in) including IFR probe; height 12.12 m (39 ft 9.2 in)
Weights: empty «quipped 86000 kg (189,594 lb); maximum take-off 185000 kg |407,84B lb) Performance: maximum level speed 925 knh (575 mph); climb to 5000 m (16,405 ft) in 13 minutes, service ceiling 12000 m (39,370 ft); combat radius 5400 km (3.977 miles) Armament: twin NR-23 23-mm cannon in ‘ail turret; maximum ordnance 11340 kg (25.003 lb)