Dassault Mirage F1

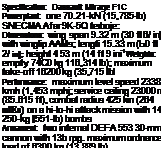 |
 |
|
D |
espite its suffix, the Mirage F1C was the initial production version of Dassault’s successor to its highly successful Mirage ІП/5 delta. It was deve ooed to meet ап Агтёе de ҐAir fAA) require merit for an all-weather interceptor. Forsaking the Mirage Ill’s delta configuration *’or a high-mounted wing and conventional tail surfaces, the prototype first flew on 23 December 1966, Mirage F1C production deliveries to the AA began in May 1973. The initial 83 aircraft were followed by 79 Mirage F1C-20Qs with fixed refuelling probes (necessitating a small fuselage plug), The AA also received 20 Mirage F1B tandem-seat trainers which retained their Tull combat capability.
Dassault converted 64 F1C-200S to serve as dedicated tactical reconnaissance platforms. These Mirage F1CR-200s arc equipped with an infra-red linescan unit, undernose cameras and centreline pods for SLAR, LOROP or Elint equipment. They also have a modernised cockpit with a Martin-Baker Mk 10 ejection seat, new RWR and two additional underwing hardpoints for chaff/flare dispensers. The F1CR fleet is now being equipped with the PRESTO stand-off reconnaissance pod, replacing the interim DFSIRF system.
The Mirage F1CT (T-Tactique) was a logical product of the shortfall in French ground attack capability and a surplus of air defence fighters following Mirage 2000C deliveries. From 1991, 55 Mirage FICs were converted to F1CT standard
France’s dual-role Mirage FICRs are tasked with reconnaissance and attack missions, and had their combat dehut in 1991, during Desert Storm.
have peer given expanded tactical capability with a laser rangefinoer. improved RWR and chaff/f:are dispensers. FlCTs are most often deployed with the French units still based in Africa. The last remaining AA F1C squadron is also based in Africa, with IEC4/33 in Djibouti,
The Mirage F1 has been widely exported. F1Cs were sold to Soutn Africa (F1CZ. now withdrawn), Morocco (F1CH), Jordan (F1CJ), Kuwait (F1CK, F1CK2. now withdrawn), Greece (F1CG) and Spain (F1CEK The Mirage F1A was a simplified version for day visual attack missions, equipped with the Aida II ranging radar in a reprofiled nose. It was sold to Libya (FIADi and South Africa (F1AZ fitted with a laser-ranger, now withdrawn).
The Mirage FlE (and corresponding Mirage FID trainer) was an upgraded multi-role fighter/attack version for export, fitted with an INS. central nav/attack computer and HUD. F1Es were exported to Ecuador (F1JA/E), Iraq (F1EQi. Jordan (F1EJ), Libya (FlED), Morocco (FlEH and FlEH-200), Qatar (FIEDA and F1DDA) and Spain (F1EE-200)
Between 1999 and 2001 Spain’s 52 Mirage F1s received a cockpit upgrade adding new communications, self – defence and navigation systems
 |
For the third Mirage generation, Dassault returned to the delta configuration, using negative longitudinal stability and a fly by-wire flight control system to eliminate many of the shortcomings of a conventional delta – As such, the Mirage 2000 has its predecessor’s large internal volume ano low wave drag, but has improved agility, slow-speed handling and lower landing speed. The first of five prototypes was initially flown on 10 March 1978. The first of 37 production Mirage 2000Cs made its maiden flight on 20 November 1982 and deliveries began in April 1983, with IOC in July 1984. All eariy production 2000C-S2. – S3 aircraft had SNECMA M53-5 engines, and introduced successive improvements to the Thomson-CSF RDM radar. The Mirage 2000C-S4 and – S5 introduced the uprated M53-P2 powerplant and the superior RDI radar optimised for look- down/shoot-down intercepts with two MATRA Super 530D missiles. With RDM radar, Mirage 2000Cs carried Super 530F and Magic 1 missiles.
Export versions of the RDM-equipped, M53-P2- powered variant have been delivered to Abu Dhabi (Mirage 2000EAD, 22 aircraft), Egypt (Mirage 2000EM, 16), Greece (Mirage 2000EG, 36), India (Mirage 2000HS Vajra, 46) and Peru (Mirage 2000P 10).
The Mirage 2000B tandem two-seat trainer first flew in August 1983. It loses some internal fuel and both cannon in order to accommodate the second cockpit. Abu Dhabi’s two-seat trainers are known as Mirage 200QDADs, India’s are Mirage 2000THs and Peru’s are Mirage 2000DPs. The reconnaissance-configured Mirage 2000R has a radar nose and carries podded sensors: multi-camera, sidelooking airborne radar, and long-range optical. Abu Dhabi has acquired eight Mirage 2000RADs
The upgraded Mirage 2000-5 introduces an advanced five-screen cockpit display. Mica AAMs, RDY multi-mode radar, and advanced self-protection suite and additional avionics. The 2000-5 is aimed largely at the export market, and significantly improves the basic aircraft’s combat capability. The French air force is also acquiring the Mirage 2000-5F through the conversion of 37 of its existing 2000Cs. The first converted prototype flew on 26 February
1996. The first export customer for the -5 came in 1992 when Taiwan ordered 60 Mirage 2000-5Els (including 12 2000-5DI trainers). Deliveries began in
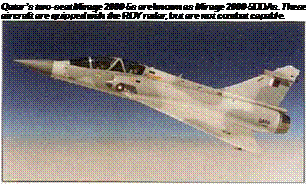
1997. Other orders have come from Qatar (12 Mirage 2000-5EDA/DDAs). Abu Dhabi (UAE) and Greece are acquiring a further improved version the Mirage 2000-5 Mk II. also referred to as the Mirage 2000-9
 Specification: Dassault Mirage 2000-5 Powerplant: ore 95.12-kN (21,384-lb) SNECMA M53-P2 turbofan Dimensions: wing span 9,13 m (29 ft 112 in); length 14.36 nr. (47 ft 1И in): height 5 20 m (17 ft/in)
Specification: Dassault Mirage 2000-5 Powerplant: ore 95.12-kN (21,384-lb) SNECMA M53-P2 turbofan Dimensions: wing span 9,13 m (29 ft 112 in); length 14.36 nr. (47 ft 1И in): height 5 20 m (17 ft/in)
Weights: empty /500 kg (16,534 lb), maximum take-off 17000 kg (37.478 lb)
Performance: maximum level speed more than 2338 kmh (1.453 mph); maximum rate of climb at sea level 17060 m (55,971 ft) par minute: service ceiling 18900 m (59.055 ft); combat range over 1480 km (920 miles) with four 250-kg bombs
Armament: two 30 mm 0EFA 554 cannon with 125 rpg: 6300-kg (13,890-lb) ordnance
|
|










