Sukhoi Su-7
Su-7B, -7BIN/I, -7BMK and -7U; NATO name "Fitter"
Origin: The design bureau of Pavel A. Sukhoi. Soviet Union.
Type: Single-seat close-support and interdiction: (-7U) dual-control trainer.
Engine: One Lyulka AL-7F turbojet rated at 15.4301b (7000kg) dry or 22.0461b (10,000kg) with maximum afterburner.
Dimensions: Span 29ft 3Jin (8-93m). length (all. incl probe) 57ft (17’37m); height (all) 15ft 5in (4-70m).
Weights: Empty (typical -7) 19,0001b (8620kg). maximum loaded (typical -7) 30.0001b (13.610kg).
Performance: Maximum speed, clean, at altitude, (all) 1.055mph (1700km/h. Mach 1 6). initial climb (-7BM) 29.000ft (9120m)/min; service ceiling (-7BM) 49,700ft (15.150m): range with twin drop tanks (all) 900 miles (1450km).
Armament: /-7) two 30mm NR-30 cannon, each with 70 rounds, in wing roots: four wing pylons, inners rated at 1.6531b (750kg) and outers at 1,1021b (500kg), but when two tanks are carried on fuselage pylons total external weapon load is reduced to 2.2051b (1000kg).
History: First flight (-7 prototype) not later than 1955: service delivery (-7B) 1959.
Users: (-7) Afghanistan. Algeria. Czechoslovakia, Egypt, ffungary, India. Iraq. N Korea. Poland. Romania. Soviet Union. Syria. Vietnam.
 |
Development: Two of the wealth of previously unknown Soviet aircraft revealed at the 1956 Aviation Day at Tushino were large Sukhoi fighters, one with a swept wing (called "Fitter" by NATO) and the other a tailed delta (called "Fishpot"). Both were refined into operational types, losing some of their commonality in the process. The delta entered service as the Su-9 and -11, described separately. The highly-swept Su-7 was likewise built in very large numbers, optimised not for air superiority but for ground
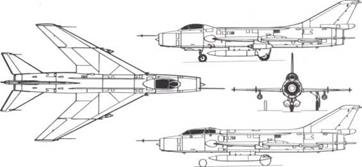
Above: Three-view of Su-7BMK, with side view (bottom) of -7U "Moujik".
attack. As such it has found a worldwide market, and despite severe shortcomings has been exported in numbers which exceed 700. All Sukhoi combat aircraft have been made within the Soviet Union The good points of the Su-7 family are robust structure, reasonable reliability and low cost: drawbacks are vulnerability to small-calibre fire and the impossibility of getting adequate field length, weapon load and radius of action all together There are many variants. The original -7B was quickly superseded by the more powerful -7BM. with twin ribbon tail chutes. The most common export model is the -7BMK with low-pressure tyres and other changes to improve behaviour from short unpaved strips. The -7U is the tandem dual trainer. Since 1964 many BMK have been seen with take-off rockets and four wing pylons.
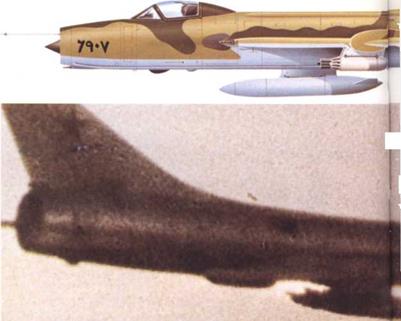
 Left: An Su-7BM of the Egyptian Air Force. Some 120 survive, despite heavy losses from many causes.
Left: An Su-7BM of the Egyptian Air Force. Some 120 survive, despite heavy losses from many causes.
Below: A frame from a Soviet propaganda film showing Su-7B type attack aircraft making passes on surface targets. The fundamental fault of this family is ability to carry fuel or weapons but not both.










