SEPECAT Jaguar
Jaguar GR.1 and T.2, Jaguar A and E, and Jaguar International
Origin: SEPECAT. consortium formed by British Aerospace (ВАС) and Dassault-Breguet, France.
Type: (GR.1, A and International (I.)) single-seat all-weather attack: (T.2 and E) dual operational trainer.
Engines: Two Rolls-Royce/ТигЬотёса Adour two-shaft augmented к turbofans: (except I.) 7.305lb (3313kg) Adour 102: (I.) 8.000lb (3630kg) Adour 804.
Dimensions: Span 28ft 6in (869m); length (except T.2, E) 50ft 11 in (15 52m); (T.2, E) 53ft 11 in (16-42m): height 16ft 1 iin (4-92m). Weights: Empty, classified but about 1 5,0001b (6800kg): "normal take-off" (ie, internal fuel and some external ordnance) 23,0001b (10,430kg): maximum loaded 34,000lb (15,500kg).
Performance: Maximum speed (lo, some external stores) 820mph (1320km/h. Mach 1-1), (hi, some external stores) 1.055mph (1700km/h. Mach 1-6): climb and ceiling, classified: attack radius, no external fuel, hi-lo-hi with bombs. 507 miles (81 5km): ferry range 2,614 miles (4210km). Armament: (A, E) two 30mm DEFA 553 each with 150 rounds: five pylons for total external load of 10,0001b (4536kg): (GR.1) as above but guns two 30mm Aden: (T.2) as above but single Aden. (International) wide range of options including increased external loads.
History: First flight (E) 8 September 1968: (production E) 2 November 1971: (production GR.1) 11 October 1972: squadron delivery (E, A) May 1972, (GR, T) June 1973.
Users: Ecuador, France, India, Oman, UK (RAF).
Development: Developed jointly by ВАС in Britain and Dassault-Breguet in France, to meet a joint requirement of the Armee de Г Air and RAF, the
|
|
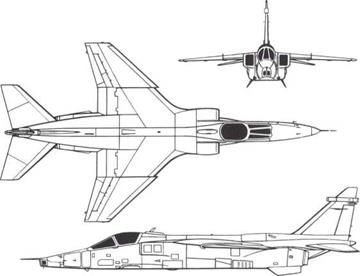
Above: Three-view of Jaguar GR.1 without stores.
Jaguar is a far more powerful and effective aircraft than originally planned and has already demonstrated unmatched capabilities in service. The original idea was a light trainer and close-support machine, with 1,3001b

continued ►

|
|

XZ358 was one of the last of the 202 Jaguars delivered to the Royal Air Force. It is a GR.1 multi-role single-seater, pictured here making an afterburning takeoff in clean condition. By late 1980 almost all the aircraft in service will be fitted with more powerful Mk 104 engines of the same thrust as the Mk 804 fitted to the Jaguar International export version.
weapon load, but with British pressure this was upgraded to today’s outstanding aircraft whose only marketing problem is the fact that the French partner prefers aircraft which appear to be all-French (yet. in fact, Dassault makes only the same proportion of the Mirage F1 as it does of the Jaguar, namely, about 50 per cent). Despite this unhappy political scene the sheer merit of the Jaguar, and the enthusiastic missionary work done by its operating units in the Armee de I’Air and RAF, is gradually winning valuable orders, beginning with Ecuador and Oman in 1974. Further sales are likely with the more powerful International version now flying. The two basic singleseat versions share a common airframe but are totally different in equipment. The French A model has a simple twin-gyro platform, doppler, and a basic navigation computer; in 1977 an Atlis laser pod was being added. The RAF GR.1 has inertial navigation, head-up display, projected map display, radar height, integrated nav/attack system and laser ranger, as well as comprehensive ECM and option of a multi-sensor reconnaissance pod. All versions can have nose radar, refuelling probe and the option of overwing pylons for light dogfight missiles (Jaguar development aircraft have flown with Matra Magics in these positions). Thanks to a dynamic programme of engine development Jaguar users have the option of various increased- thrust Adours, including the Mk 804 (Adour 26) fitted to the basic Jaguar International, and the even more powerful Adour 56 and 58 (in the 10,0001b, 4500kg class) which will be available from 1980. It is the intention of the RAF to select one of the uprated engines and convert all Jaguar engines to this standard, to gain even better field length and flight performance with large mission loads. By 1977 some 300 aircraft had been delivered, and several new customers were engaged in contract negotiation.
 Right: This Jaguar International is one of ten single – seaters (as illustrated) and two two-seaters equipping No 8 Sqn of the Sultan of Oman’s Air Force. This unit is normally based at Thumrayt, in Dhofar province, and is dedicated to long-range ground attack with various weapons and to air combat with Magic missiles on overwing pylons.
Right: This Jaguar International is one of ten single – seaters (as illustrated) and two two-seaters equipping No 8 Sqn of the Sultan of Oman’s Air Force. This unit is normally based at Thumrayt, in Dhofar province, and is dedicated to long-range ground attack with various weapons and to air combat with Magic missiles on overwing pylons.
Below: Test firing of a Matra 550 Magic close-range air-to-air missile from special overwing pylons added to a Jaguar retained for research and trials programmes by British Aerospace Warton Division. Another completed programme concerns fitting the Thomson-CSF Agave radar, and many other sensors are available as options.
|

Above: Fly-past by single-seat Jaguar A and two-seat Jaguar E aircraft of the 7e Escadre de Chasse, Агтёе de Г Air, normally based at St Dizier. This was the first Jaguar wing to be fully equipped in the French air force, with a strength of 35 single – seaters and 25 dual-control trainers with the conversion unit.













