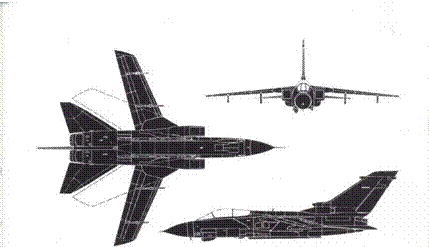
Panavia Tornado
Tornado IDS (GR.1), ADV (F.2) and dual (T.3)
Origin: Panavia Aircraft GmbH, international company formed by British Aerospace, MBB of W Germany and Aeritalia.
Type: Two-seat multi-role combat aircraft, (S) optimised for strike, (AD) for air defence, (T) dual trainer.
Engines: Two Turbo-Union RB.199 Mk 101 three-shaft augmented turbofans each rated at 1 5,000lb (6800kg) with full afterburner.
Dimensions: Span (25°) 45ft 7iin (13-90m), (65°) 28ft 2Jin (8-60m); length (IDS) 54tt 9iin (16 7m), (ADV) 58ft 9in (17-9m); height 18ft 83ІП (5-7m).
Weights: Empty, about 24,000lb (10,890kg): loaded (clean) about 35,OOOIb (15,880kg): maximum loaded, about 60,000lb (18,150kg). Performance: Maximum speed (clean), at sea level, about 910mph (1465km/h, Mach 1-2). at height, over 1,320mph (2135km/h, Mach 2): service ceiling over 50,000ft (1 5,240m): range, about 1,000 miles (1610km) on internal fuel (high, wings spread), or over 3,000 miles (4830km) in ferry mode with maximum fuel.
Armament: Two 27mm Mauser cannon in lower forward fuselage: seven pylons, two tandem on body and four on the swinging wings, for external load up to 1 8.0001b (81 65kg). ADV has only one MK27 gun, plus four Sky Flash missiles recessed under fuselage and two or four AIM-9L Sidewinder close-range missiles.
History: First flight (prototype) 14 August 1974), (production IDS) July 1979, (ADV) September 1979: service delivery (IDS to trials unit) February 1978, (squadron service, MFG) 1982.
 |
Users: W Germany (Luftwaffe, Marineflieger), Italy, UK (RAF). Development: No combat aircraft in history has ever been planned with such care by so many possible customers. Studies began in 1967, after the French had abandoned the AFVG aircraft in the same class and decided not to participate in collaborative aircraft of this type. Panavia Aircraft was registered on 26 March 1969 in Munich as a three-nation company to manage the MRCA (multi-role combat aircraft) programme, with shares
 Above: Two MBB – assembled prototypes: white-painted 04 and camouflaged 07. later joined by other pre-production machines and production IDS.
Above: Two MBB – assembled prototypes: white-painted 04 and camouflaged 07. later joined by other pre-production machines and production IDS.
held in the ratio ВАС 42J per cent, MBB 42J per cent and Aeritalia 15 per cent. In September 1969, after intense competition with the United States, the RB.1 99 was selected as the engine and a month later Turbo-Union was formed as the engine-management company with shares held in the ratio Rolls-Royce 40 per cent. MTU 40 per cent and Fiat 20 per cent. Thanks to careful planning the Tornado programme has since demonstrated that it is possible for several nations to work together to create a modern military aircraft which promises to exceed all possible rivals in mission effectiveness, versatility and low cost, having already demonstrated better mission capability than the latest competing types designed specifically for that mission. Its design missions are: close air support/battlefield interdiction: long-range interdiction/strike: naval strike: air superiority: air defence/ interception; reconnaissance; training. At one time it was planned that the three nations should develop slightly different versions with either one or two seats and dry or wet wings, but all basic aircraft now in production are identical, with two seats and sealed integral-tank wings. From stem to stern the Tornado is totally modern — a fact which its many competitors have sought to counter by claiming it to be "complicated” or "expensive".
In fact it is not possible to fly the required missions without carrying the equipment, and the fly-away price of £3-9 million (in September 1974 sterling) is by a very wide margin cheaper than any comparable aircraft. The only aircraft that bears comparison with MRCA is the larger F-14, which cannot meet the MRCA requirements in the attack and reconnaissance roles, and is officially doubted as having the capability – in the European environment — to fly the interception missions of the Tornado ADV. Other combat aircraft with a single seat and non-swinging wing are grossly deficient in all ►

Below: Prototype 02, assembled in Britain in 1974, with ‘tri-national’ markings, original tail/body fairing and camera on the front of the passive-ECM fairing.
 |
Nosing in over its home airfield – Warton, on the north shore of the Ribble estuary— the first Tornado F.2 interceptor gives a hint of its outstanding capabilities. Two engines (of amazing compactness and fuel-economy), two crew, a new advanced – technology radar, swing wings, extra fuel (in a longer fuselage), the world’s most modern sensors and cockpit displays, and Skyflash and (not fitted here) AIM-9L missiles form an unequalled combination.
|
|

roles except close-range air combat, a specialised mission for which the common version of Tornado is not intended (though its performance in this role is considerably better than a Mirage III, F-5 or F-4).
The basic Tornado has highly compact and efficient engines of extremely advanced design, with automatically scheduled inlets and nozzles. Flight control is by large tailerons, augmented at low sweep angles by wing spoilers; the system is fully digital and signalled by quad fly-by-wire via an automatic command and stability augmentation system. For high lift at low speeds the wings have full-span slats and double-slotted flaps. Other equipment includes a mapping radar, terrain-following radar and computer, and laser target ranger for extreme accuracy. ECM and other penetration aids are exceptional. Planned production for the three original partners comprises 809 aircraft, of which 385 will be for the RAF, 202 for the Luftwaffe (replacing the F-104G and G91 R), 122 for the Marineflieger (replacing the F-104G) and 100 for the Regia Aeronautica (replacing the F-104G and G91Y) in all roles. The variety of external stores to be carried by MRCA exceeds that for any other aircraft in history, embracing almost every airborne store of three major nations in virtually all combat roles. A proportion of aircraft for the first three customers will be dual trainers (the first flew on 5 August 1 975) which retain all the fuel capacity and weapons of singlepilot versions.
Of the RAF total of 385, about 220 will be of the common IDS (inter-

Above: Initial gun-firing trials took place in April 1978 with prototype 06 (the gun had been air-tested in a Lightning).
Left: Another photograph of 06, which was the first to fly stores – separation tests, a task completed in March 1976.
Below: First launch from Tornado of a Kormoran anti-ship guided missile took place from 09 at Decimomannu in July 1978.
|
|
diction strike) variant: the other 165 will be of the ADV (air-defence variant) type, planned to replace the Phantom in the air defence of the UK, Commonality with the IDS aircraft is officially put at 80 per cent, differences mainly being confined to the forward fuselage though the wing-root gloves have acute sweep and no Kruger flaps. Engines are unchanged, though higher-thrust versions are available on customer request. The ADV fuselage is longer partly to accommodate Sparrow or Sky Flash missiles nose-to-tail and partly to accommodate much additional fuel. The radar is a completely new Marconi Foxhunter set, with planar scanner by Ferranti inside a more pointed radome which reduces drag. Computer and radar programs are quite different from those of the IDS, though each version has considerable capability in the primary role of the other. Great attention has been paid to the ADV target identification and vision-augmenting subsystems, to make full use of the range of the radar and Sky Flash missile. The radar homing/ warning installation is also new, and quite different from equipment fits used on the IDS version.
In mid-1979 the 16 prototype and pre-production Tornados had flown and been succeeded by the first few production machines (the first two being dual-pilot versions with full operational capability) and the first ADV prototypes. At that time three contracts for production batches had been signed for a total of 314 aircraft for inventory service with the four initial customers.












