The Mir complex core in flight.
The Mir complex core. The core was equipped with six docking assemblies and a new docking system.

|
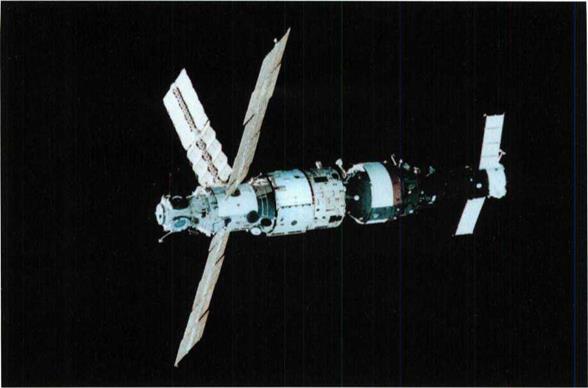
The Mir complex core with the Kvant module and the SoyuzTM spacecraft in flight.
|
|
|

The launch of the Mir complex core. The launch was accomplished with the use of the Proton launch vehicle on February 20, 1986.
|
|
|

The Soyuz launch vehicle flight.
|
|
|
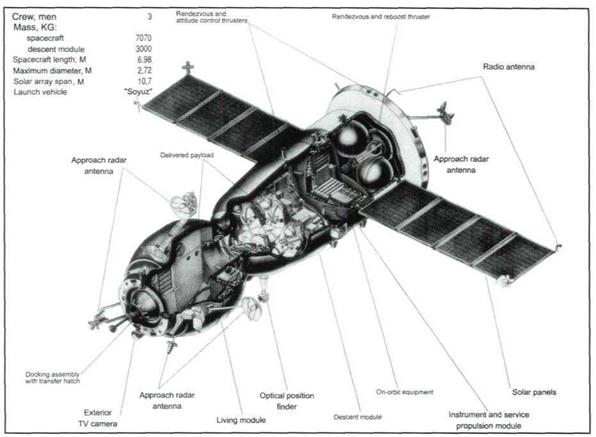
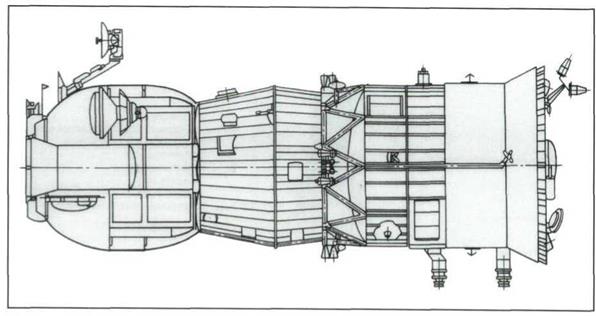
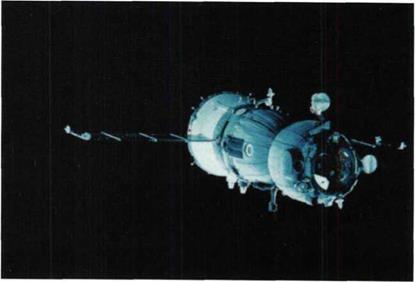
The SoyuzTM spacecraft intended for delivery and change of the crew on the Mir complex.
|
|
|

Installation of the Soyuz launch vehicle with SoyuzTM spacecraft onto the launching pad.
|
|
|
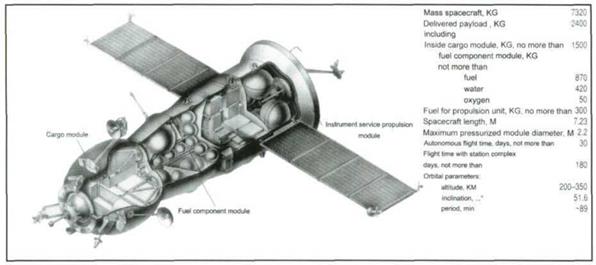
The Progress M cargo spacecraft intended for delivery of fuel and other consumables to the Mir complex.
|
|
|
An international crew on board the Mir complex.
|
 Launch of the Soyuz launch vehicle with the Progress M cargo spacecraft.
Launch of the Soyuz launch vehicle with the Progress M cargo spacecraft.
|
The Progress M spacecraft equipped with the recovery ballistic capsule.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
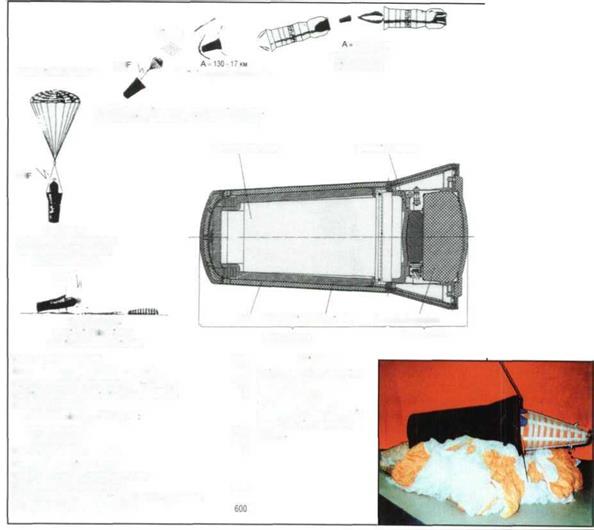
Ballistic capsule descends
|
|
|
The recovery ballistic capsule made it possible to deliver results of investigations carried out by cosmonauts on board the Mir complex back to Earth.
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H * 4,5-3 KM
Separate braking parachute
deploy primary parachute
with pressure relay
|
|
|
|
|
The recovery ballistic capsule with the parachute in the RSCE museum.
|
|
|
|
|
Thermal insulation a = 40
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Mass capsule (max). KG Mass returning payload. KG. no more than Cargo spacecraft retrograde bum (AVt). M/S Velocity of descent on pnnopal parachute. M/S Touchdown precision
( aVt *150 m s. Hort, ‘350 км), km along the route lateral spread
Time lo detection by base, hrs
Expected flow retneved cargo
by rapid retrieval 2-3 capsules per year
(1991-1994). KG. not more than
Payload recovery opportunities on 11F732 spacecraft
(12 spacecraft), KG. not more than
|
|
|
|
Objectives
Quick return of self-financing projects and commercial contracts in the area of technology, biology, photography (films, magnetic tapes, kits with experiment results)
|
|
|
|

|
Cargo spacecraft Progress M
|
|
|
Crew, men Mass. T: station
research instruments and equipment Nominal electrical power system capacity kW Orbital parameters attitude. KM inclination,*
Attitude precision using gyrodynes.
|
|
|
Astrophysics module Kvant
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Station equipment module "Kvant-2"
|
|
 |
|
Manned spacecraft Soyuz TM
|
|
|
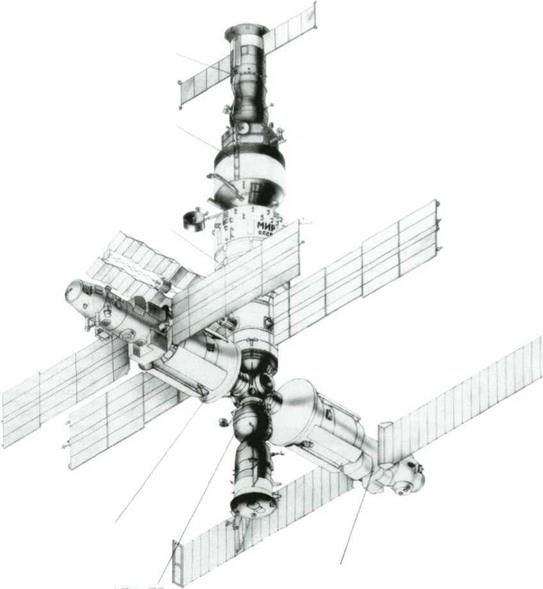
The arrangement of modules on the Mir orbital complex core.
|
|
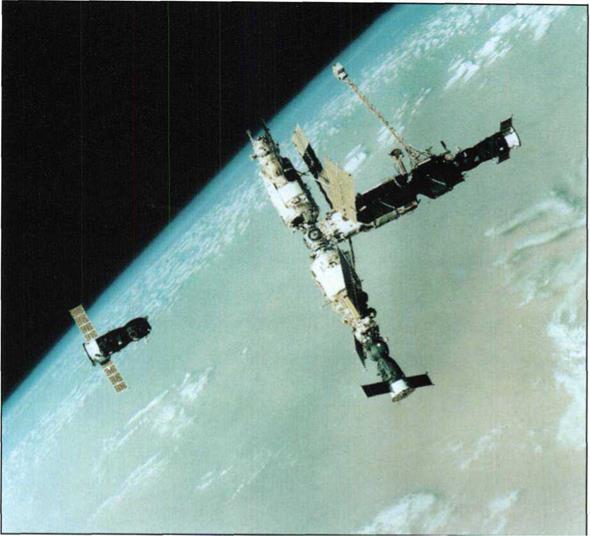
 The Mir complex with the Kvant, Kvant-2 and Kristall modules, transport spacecraft Soyuz TM – 16, cargo spacecraft Progress M – 17 and undocked cargo spacecraft Progress M-18. The picture was taken from the Soyuz TM-17 transport spacecraft on July 3, 1993.
The Mir complex with the Kvant, Kvant-2 and Kristall modules, transport spacecraft Soyuz TM – 16, cargo spacecraft Progress M – 17 and undocked cargo spacecraft Progress M-18. The picture was taken from the Soyuz TM-17 transport spacecraft on July 3, 1993.

 Launch of the Soyuz launch vehicle with the Progress M cargo spacecraft.
Launch of the Soyuz launch vehicle with the Progress M cargo spacecraft.




![]()
 The Mir complex with the Kvant, Kvant-2 and Kristall modules, transport spacecraft Soyuz TM – 16, cargo spacecraft Progress M – 17 and undocked cargo spacecraft Progress M-18. The picture was taken from the Soyuz TM-17 transport spacecraft on July 3, 1993.
The Mir complex with the Kvant, Kvant-2 and Kristall modules, transport spacecraft Soyuz TM – 16, cargo spacecraft Progress M – 17 and undocked cargo spacecraft Progress M-18. The picture was taken from the Soyuz TM-17 transport spacecraft on July 3, 1993.

















