Lunar Manned Program activities
In accordance with the lunar manned program, the NI – L3 system was designed, which included the Nl three-stage rocket and L3 lunar complex.

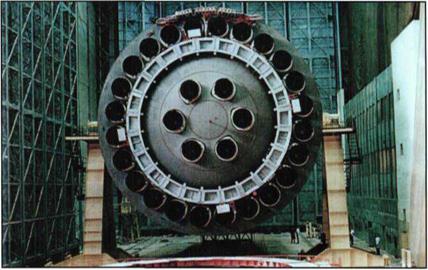 |
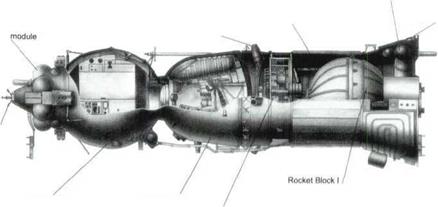
The maximum diameter of the block is 16.8 meters (dimensions taken by stabilizers are 22.33 meters) with a height of 30.1 meters. The block houses 30 engines with ground thrust of 153 tons each.
 The V block was used as the third stage. Maximum diameter of the block is about 7.6 meters with the height (by the interfaces) being I 1.5 meters. The block houses four engines with a vacuum thrust of 41 tons each.
The V block was used as the third stage. Maximum diameter of the block is about 7.6 meters with the height (by the interfaces) being I 1.5 meters. The block houses four engines with a vacuum thrust of 41 tons each.
|
|
The B block was used as the second stage of the N I rocket. The maximum diameter of the block is about 10.3 meters with a height of 20.5 meters. The block houses 8 engines with a vacuum thrust of 180 tons each.
|
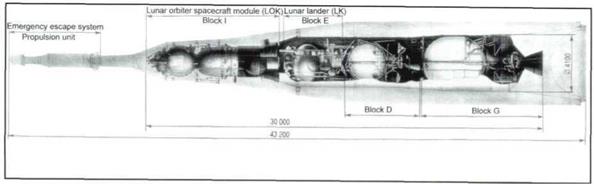
The L3 lunar rocket complex including G and D rocket blocks, the lunar orbiter with the I rocket block and the lunar vehicle with E rocket block.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
 Rendezvous and attitude control thruster
Rendezvous and attitude control thruster
Crew, men 2
Maximum flight time, days 13
Mass. KG
Spacecraft in orbit (Artificial Lunar Satellite) 9850
Spacecraft before launch back to Earth 7530
Descent apparatus 2804
Module I parameters
Boost thruster (double chamber)
Thrust. KGF 3388
Specific thurst. KGF-S/KG 314
Rendezvous and reboost thruster
 Thrust. KGF 417
Thrust. KGF 417
Specific thrust. KGF-S/KG 296
Fuel capacity. KG
Nitrogen Tetroxide (Oxidizer) 2032
Unsymmetrical dimethyl hydrazine 1120
Dimensions. MM
Length 10 060
Maximum diameter hud 2930
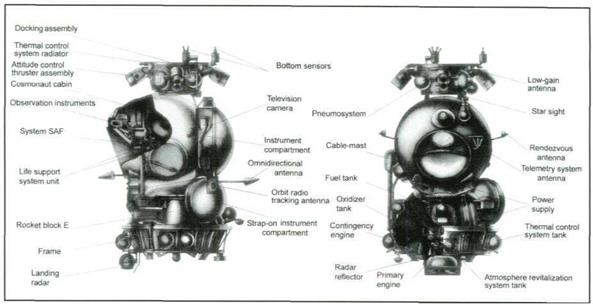
The lunar orbiter including the habitation compartment and the vehicle to be descended to Earth, as well as the I rocket unit, and the instrumentation and service module. The orbiter mass in ALS orbit is 9,850 kg. Maximum length is about 10 meters, diameter being 2.9 meters.
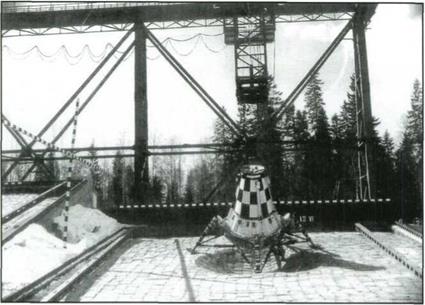
The lunar orbiter on the mounting bogie.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
![]()
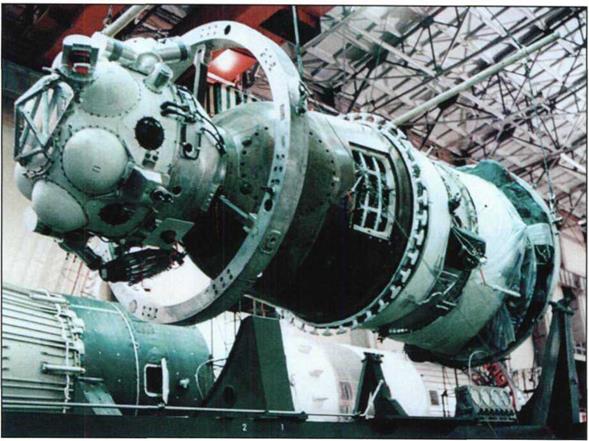
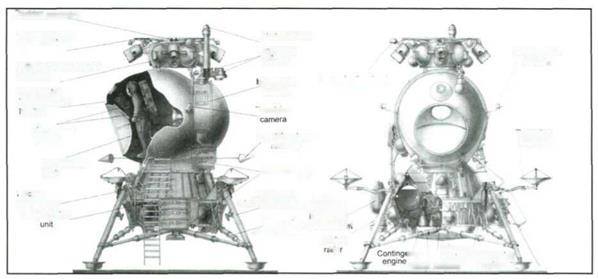
The lunar vehicle consisting of the lunar descent assembly, the cosmonaut’s cabin with various systems, and the E rocket unit with main and stand-by engines.
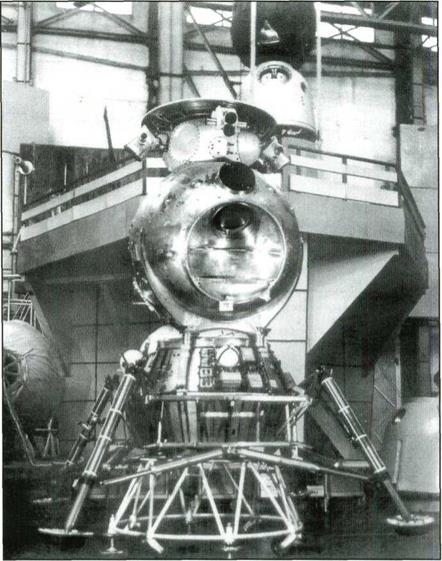 The lunar vehicle in the shop.
The lunar vehicle in the shop.
|
 The
The
7K-LIS
unmanned
spacecraft
in the
assembly
 jig-
jig-
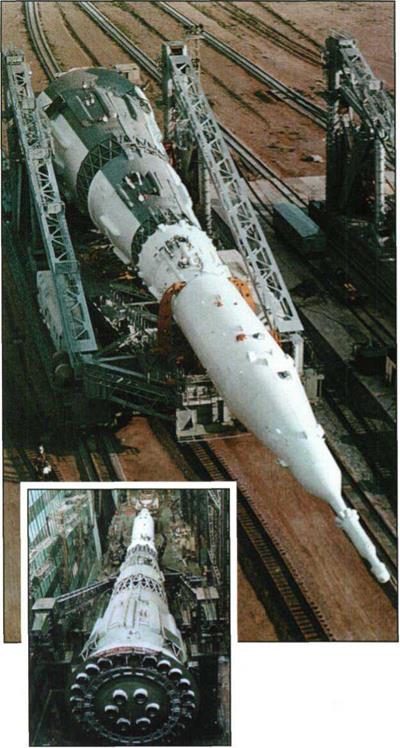 |
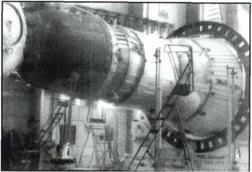
 The NI-L3 space system on the transport-erecting assembly in the assembly building, ready for roll-out to the launch area.
The NI-L3 space system on the transport-erecting assembly in the assembly building, ready for roll-out to the launch area.
 The NI-L3 system is erected vertically on the launcher. The transport – erecting assembly is not moved away.
The NI-L3 system is erected vertically on the launcher. The transport – erecting assembly is not moved away.
Erection of the NI-L3 system on the launcher.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
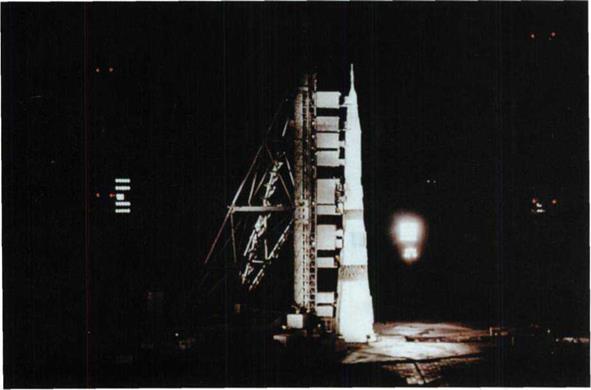
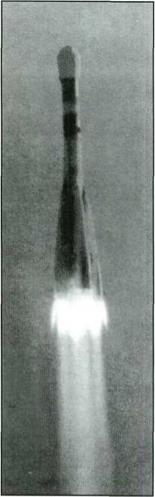
Launch of the NI-L3 system. |
|

 |
|||
 |
|||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
![]()
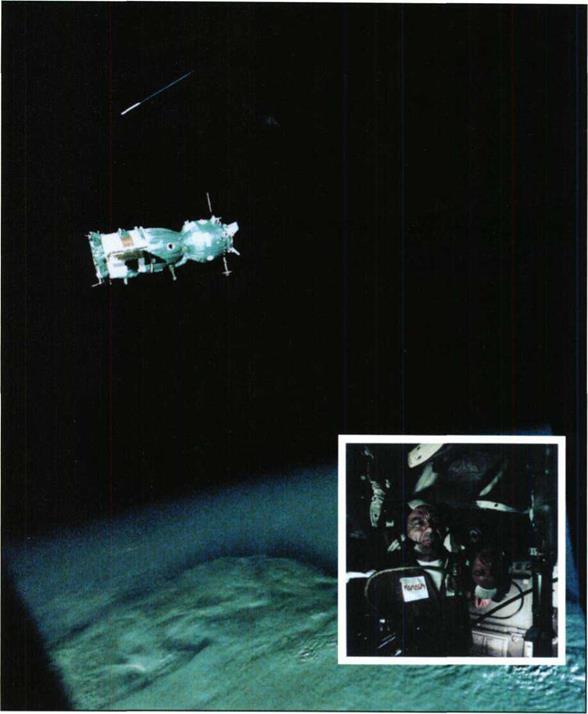
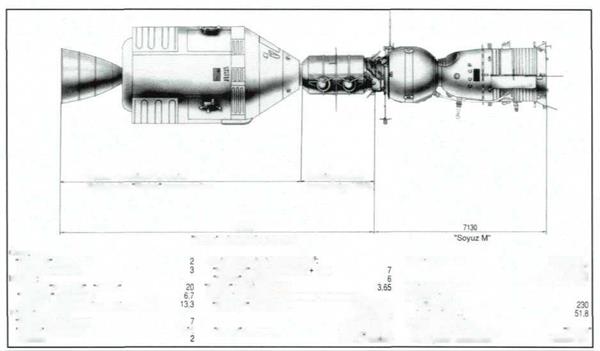
The Soyuz and Apollo spacecraft. In the summer of 1975, spacecraft from two countries docked in near-Earth space for the first time.
|
|
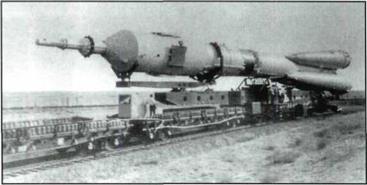
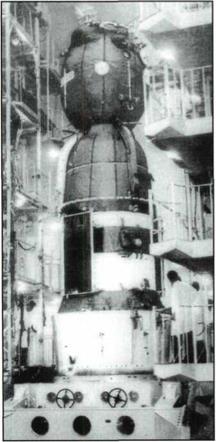 Transportation of the Soyuz launch vehicle with the Soyuz-19 spacecraft to the launching area.
Transportation of the Soyuz launch vehicle with the Soyuz-19 spacecraft to the launching area.
The Soyuz-19 spacecraft, which took part in the joint space flight according to the ASTP, in the assembly-test building being prepared for flight.
|
A view of the Soyuz spacecraft from the The crew on board the docked Soyuz and APoll° spacecraft. Apollo spacecraft. |
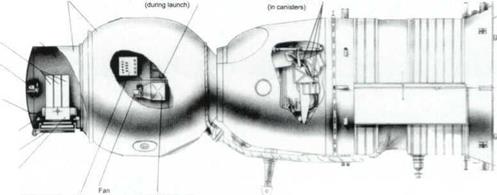
Photo compartment Multi-layer insulation 2B-30 Rim cassette Film containers
![]()
![]()

window (New model)
tsk 201 13000 i Diameter 420 мм
 |
Roll* of film Fan
The Soyuz-22 spacecraft (which is modified from the back-up spacecraft in ASTP) to be launched as part of the Intercosmos program, was equipped with the MKF-6 multizone photographic camera to test the methods and means of studying geological and geographical characteristics of the Earth’s surface from space for the benefit of national economy and environmental control.