Combat Missiles Designed in OKB-1
The R-9 missile in flight. Its launch took place on April 9, 1961. In 1964 the missile complex was introduced into the inventory.
 The RT-2 missile (left) was the first intercontinental solid-propellant missile. Its first launch took place on February 26, 1966. In 1968 the missile was added to inventory.
The RT-2 missile (left) was the first intercontinental solid-propellant missile. Its first launch took place on February 26, 1966. In 1968 the missile was added to inventory.
 The RT-I missile (right). The first strategic solid-propellant missile. Its first launch took place on April 28, 1962.
The RT-I missile (right). The first strategic solid-propellant missile. Its first launch took place on April 28, 1962.
|
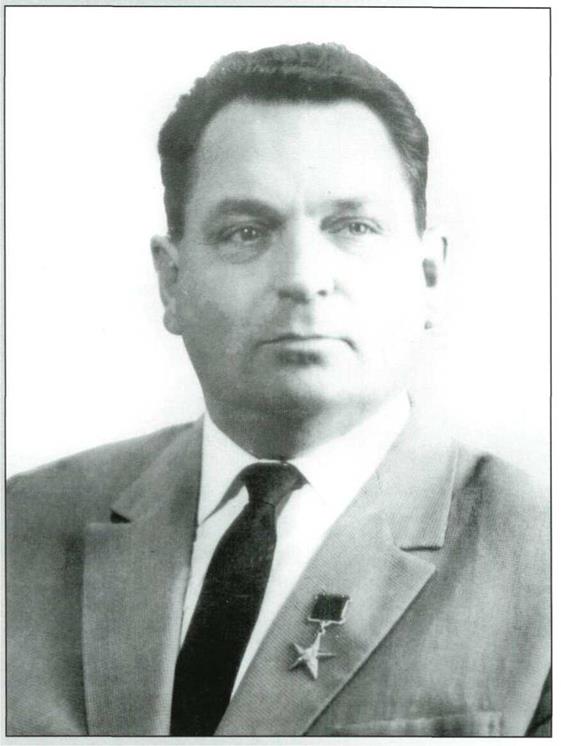

Vasily Pavlovich Mishin
Chief designer of OKB-I from 1966 until May 1974
 |
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||

![]()
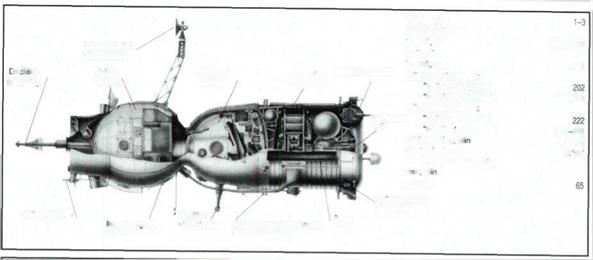
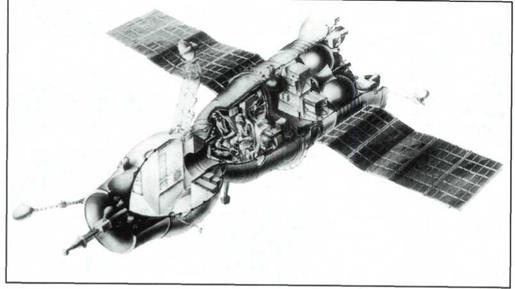 The Soyuz spacecraft (7K-OK) designed to execute a wide variety of tasks, including automatic and manual rendezvous, and docking with orbital spacecraft and stations.
The Soyuz spacecraft (7K-OK) designed to execute a wide variety of tasks, including automatic and manual rendezvous, and docking with orbital spacecraft and stations.
|
The Soyuz spacecraft on the mounting bogie.

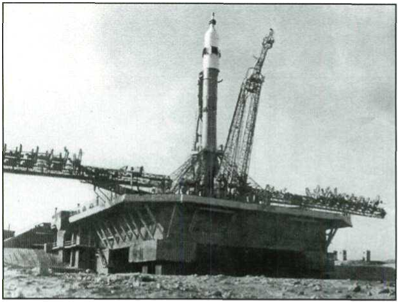 |
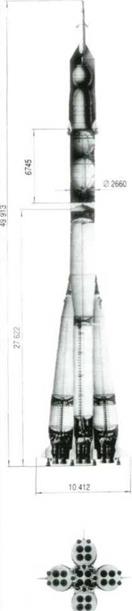
The Soyuz launch vehicle (I I AS I I). The rocket houses the emergency crew recovery system which makes it possible to move the descent vehicle away from the rocket in distress.
|
|
|
|
|


 Instrument propulsion module Descent module i Orbital module Docking module
Instrument propulsion module Descent module i Orbital module Docking module
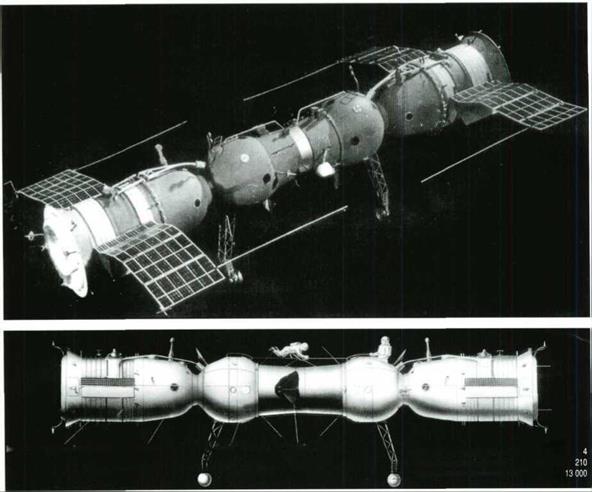
The Soyuz spacecraft (7K-OK.) docking in orbit (top). The first docking of the Soyuz spacecraft was carried out in the automatic mode during the flight of the Cosmos-186 and Cosmos-188 unmanned spacecraft.
The Soyuz spacecraft docking in orbit. The Soyuz-4 and Soyuz-5 manned spacecraft docked on January 15, 1969. Cosmonauts transferred from one spacecraft to the other through space.
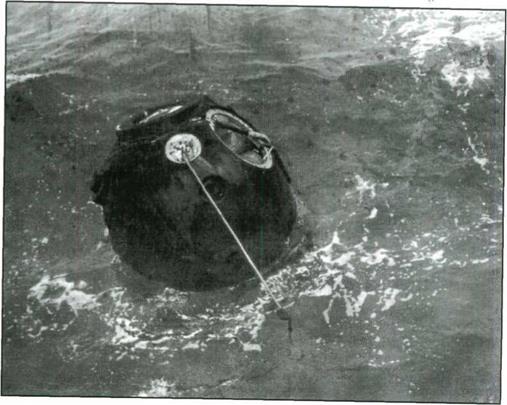
The Soyuz descent vehicle after landing.
 |
 |
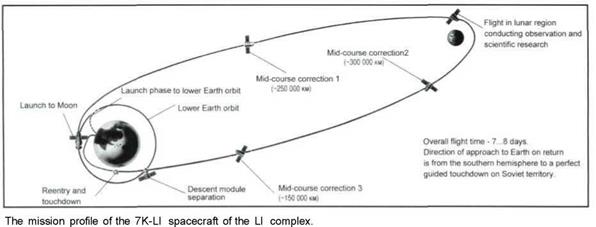
The first flight to the Moon with return to the Earth
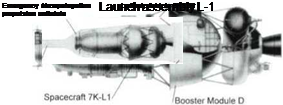
The LI space complex for the circumlunar fly-by. This complex flew five times under the name of Zond. The complex flown used the D block rocket using multiple engine I I D58 firings
|
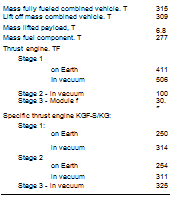
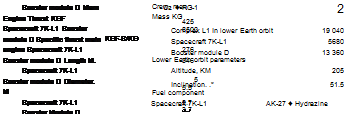
Mass station. T |
5,5 |
|
Length, M |
4.5 |
|
Diameter. M |
2.2 |
|
Minimum distance |
|
|
from lunar surface at fly-by, KM |
2000 |
|
Total flight time, days |
7 |
 |
The Zond automatic station.
![]()
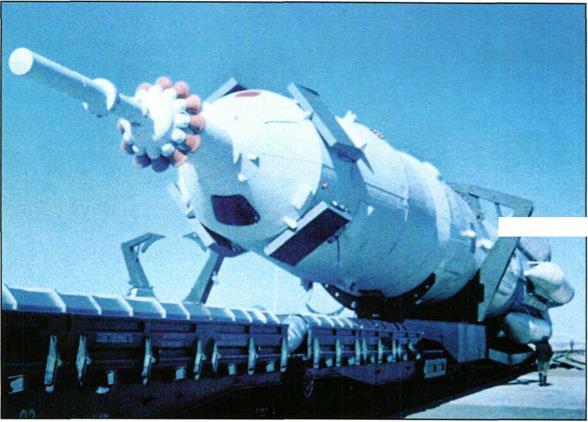
Transportation of the LI complex to the launch area.
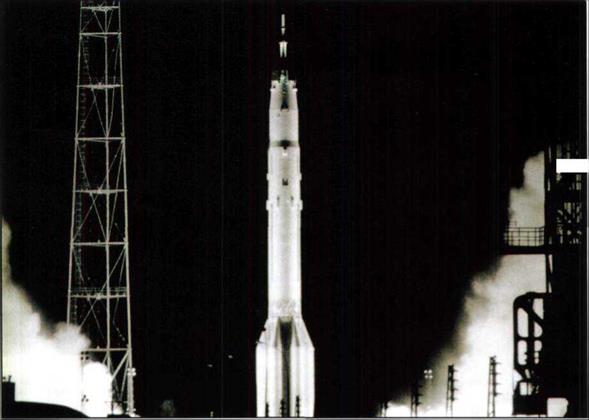
 The Proton launch vehicle with the LI complex on the launch pad.
The Proton launch vehicle with the LI complex on the launch pad.
|

 The close-cycle liquid fuel rocket engine I ID58M of TsKBEM development. This engine of 8.5 tons thrust uses oxygen and hydrocarbon fuel as propellant components. It was the world’s first engine to provide multiple in-flight firing.
The close-cycle liquid fuel rocket engine I ID58M of TsKBEM development. This engine of 8.5 tons thrust uses oxygen and hydrocarbon fuel as propellant components. It was the world’s first engine to provide multiple in-flight firing.

|
|
|