STS-62
 1994-015A 4 March 1994
1994-015A 4 March 1994
Pad 39B, Kennedy Space Center, Florida 18 March 1994
Runway 33, Shuttle Landing Facility, Kennedy Space Center, Florida
OV-103 Discovery/ET-62/SRB BI-064/SSME #1 2031;
#2 2109; #3 2029
13 days 23hrs 16 min 41 sec
Discovery
United States Microgravity Payload (USMP)-2; Office of Aeronautics and Space Technology-2 payload
Flight Crew
CASPER, John Howard, 50, USAF, commander, 3rd mission Previous missions: STS-36 (1990); STS-54 (1993)
ALLEN, Andrew Michael, 38, USMC, pilot, 2nd mission Previous mission: STS-46 (1992)
THUOT, Pierre Joseph, 38, USN, mission specialist 1, 3rd mission Previous missions: STS-36 (1990); STS-49 (1992)
GEMAR, Charles Donald (“Sam”), 38, US Army, mission specialist 2, 3rd mission
Previous missions: STS-38 (1990); STS-48 (1991)
IVINS, Marsha Sue, 42, civilian, mission specialist 3, 3rd mission Previous missions: STS-32 (1990); STS-46 (1992)
Flight Log
The 11 March launch attempt was postponed at the T — 11 hours mark when the forecast indicated that the weather would not clear in time for the launch. The launch itself proceeded without a problem, but the retrieval of the SRBs and their parachutes was delayed by two days as the recovery ships could not be deployed due to high seas.
This was the second flight under the USMP programme and the payload also featured the OAST-2 package. The OAST-1 package flew on STS-2 in 1981 and included Earth observation experiments, but this time the six experiments focused on space-related technology with potential application for satellites, circuits, sensors, processors and the International Space Station. The USMP-2 payload comprised five experiments that focused on the effects of the microgravity environment on materials and fundamental sciences. The experiments included the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace, the Critical Fluid Light Scattering Experiment,
|
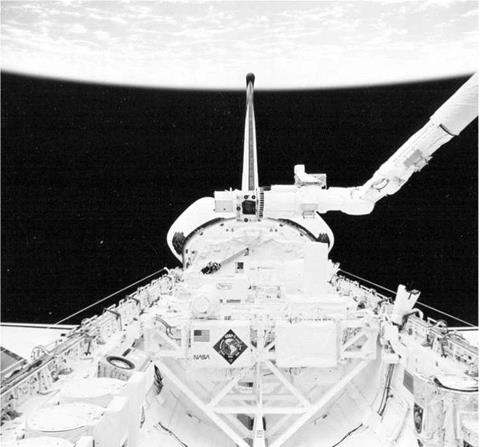
Located in the payload bay are elements of USMP-2 and OAST-2 experiments. Also in frame is the RMS used during activities featuring the Dexterous End Effector, a series of operations and observations of the RMS in one-hour sessions to develop improvements to RMS operating techniques |
the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment, Materials for the Study of Interesting Phenomena of Solidification on Earth and in Orbit and the Space Acceleration Measurement System. On orbit, the crew would activate both the USMP-2 experiments and the OAST-2 package, but they would be controlled by investigators and controllers on the ground at the Marshall Spacelab Mission Operations Control Center. USMP-2 was the main focus of the early part of the STS-62 mission, before the orbit of Columbia was lowered by about 20 nautical miles to favour the OAST package more. By flying the orbiter with an EDO pallet and in a gravity gradient mode, this flight was another step towards future space station research operations.
While the payload bay experiments were being manipulated via the ground, the crew focused on the mid-deck and other payload bay investigations. The Shuttle
Solar Backscatter UV/A and Limited Duration Space Environment Candidate Material Exposure experiments were in the payload bay, while on the mid-deck, further research was conducted in protein crystal growth, generic bioprocessing, zero-gravity dynamics, auroral photography and Earth observations, keeping the crew busy. In addition, the crew were occupied with evaluating the Dexterous End Effector, a new magnetic grapple fixture that was being evaluated in space for possible use on future RMS operations. The astronauts also completed a programme of biomedical activities, linked to the Extended-Duration Orbiter Medical Project, aimed at providing a better understanding of, and baseline data for, counteracting the effects of prolonged orbital space flight.
Milestones
168th manned space flight
91st US manned space flight
61st Shuttle mission
16th flight of Columbia
2nd flight of USMP payload
3rd Extended-Duration Orbiter (EDO) mission











