Tupolev Tu-144
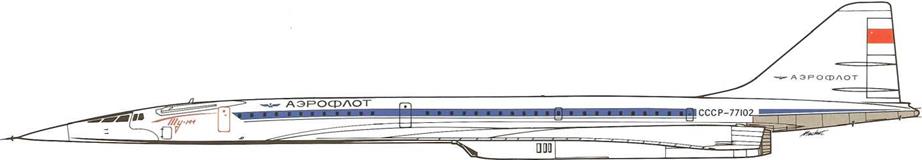 60-70 SEATS ■ 2,500km/h (l,500mph)
60-70 SEATS ■ 2,500km/h (l,500mph)
Kuznetzov NK-144 (4 x 20,000kg, 44,0001b) ■ MTOW 180,000kg (397,0001b) ■ Normal Range 3,500km (2,200mi)
|
|
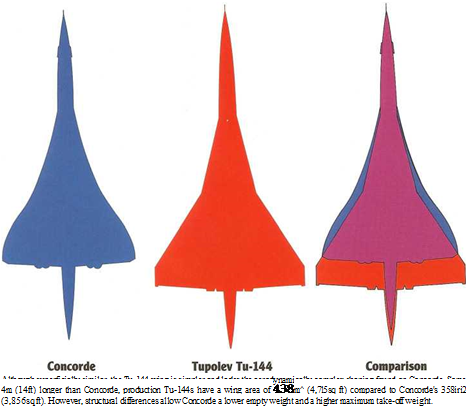 Given a specific set of performance and operational parameters, designers are usually faced with few options. Thus, at first glance, western observers tended to conclude the Tu-144 was a direct copy of the Concorde. Closer scrutiny reveals that the Tu-144 was the result of independent thinking by Andrei Tupolev’s design bureau, the most noticeable external differences to Concorde being the wing planform as shown here, and the grouping of the engines underneath the fuselage. An impressive machine by any standard, despite a lengthy gestation in three considerably diverse versions, the Tu-144 was unable to achieve sustained commercial service. However, two Tu-144s are currently in use for ozone research flights from Zhukovskiy, home of the Central Aerohydrodynamics Institute (TsAGI), near Moscow.
Given a specific set of performance and operational parameters, designers are usually faced with few options. Thus, at first glance, western observers tended to conclude the Tu-144 was a direct copy of the Concorde. Closer scrutiny reveals that the Tu-144 was the result of independent thinking by Andrei Tupolev’s design bureau, the most noticeable external differences to Concorde being the wing planform as shown here, and the grouping of the engines underneath the fuselage. An impressive machine by any standard, despite a lengthy gestation in three considerably diverse versions, the Tu-144 was unable to achieve sustained commercial service. However, two Tu-144s are currently in use for ozone research flights from Zhukovskiy, home of the Central Aerohydrodynamics Institute (TsAGI), near Moscow.
 |
THE TUPOLEV TU-144 AND CONCORDE COMPARED
|
First Flight Date |
First Service Date |
Aircraft Type |
Dimensions-m(ft) |
Speed km/h (mph) |
Seats |
MTOW kg (lb) |
Normal Range km (mi) |
First Airline |
No. Built |
|
|
Length |
Span |
|||||||||
|
31 Dec |
26 Dec 19752 |
Tupolev |
65.7 |
28.8 |
2,500 |
60-70 |
180,000 |
3,500 |
Aeroflot |
174 |
|
19681 |
1 Nov 19773 |
Tu-144 |
(216) |
(95) |
(1,500) |
(397,000) |
(2,200) |
|||
|
2 Mar |
21 Jan 1976 |
ВАС-Aero- |
61.6 |
25.6 |
2,150 |
100 |
185,000 |
6,400 |
British |
205 |
|
1969 |
spatiale |
Airways |
||||||||
|
Concorde |
(202) |
(84) |
(1,350) |
(408,000) |
(4,000) |
Air France |
 |

 |
 THE FIRST ANTONOV FREIGHTERS
THE FIRST ANTONOV FREIGHTERS
|
First Flight Date |
First Service Date |
Aircraft Type |
Dimensions-m(ft) |
Speed km/h (mph) |
Cargo Capacity kg (lb) |
MTOW kg (lb) |
Normal Range km (mi) |
No. Built |
|
|
Length |
Span |
||||||||
|
1958 |
18 Feb |
Antonov |
33 |
38 |
580 |
20.000 |
61,000 |
3,600 |
300? |
|
1965* |
An-12B |
(109) |
(125) |
(360) |
(44,090) |
(134,480) |
(1,940) |
||
|
27 Feb |
1968 |
Antonov |
58 |
64 |
600 |
88,000 |
250,000 |
5,000 |
551 |
|
1965 |
An-22 |
(190) |
(211) |
(380) |
(194,00) |
(550,000) |
(3,125) |
|
Notes: * Earlier service with WS/VTA (Soviet Air Force/Transport Command) 1 Not including prototypes |
 |
 |
Kuznetzov NK-12MA (4 x 15,000shp) ■ MTOW 250,000kg (551,1601b) ■ Normal Range 5,000km (3,100ml)
![]()


The World’s Largest
The four-engined Antonov An-22, complete with contra-rotating propellers, made it first flight on 27 February 1965, and four months later, on 15 June 1965, it made its international debut at the Paris Air Show, to the wonderment of the world. Habitually critical, sometimes disdainful, of the products of the Soviet aircraft industry, western observers were forced to take notice. Quite simply, this was a huge airplane.
It weighed 250 tons and had a payload of 100 tons. It could carry large battle tanks such as the T-62, the T-72, or the T-80, which did not complain against the customary lack of pressurization in the main cargo hold. The rear-end loading door was a neat device that not only provided the ramp, but could also form an extension to the rails along the sides of the hold, carrying the ten-ton load gantry crane. The floor was of reinforced titanium.
Following time-honored tradition, even this mammoth machine could be used on rough strips. Such extraordinary performance was made possible by an extraordinary landing gear. In each of the two fuselage fairings were three tandem wheels, for a total of twelve, to spread the load; and the tire pressure could be controlled during flight.
An Antonov An-22 prototype (SSSR-56391) on take-off. (Boris Vdovienko)
|
|
Antonov An-22 SSSR-09344 offloading relief supplies at Moscow-Sheremetyevo in April 1992. (Malcolm Nason)
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|